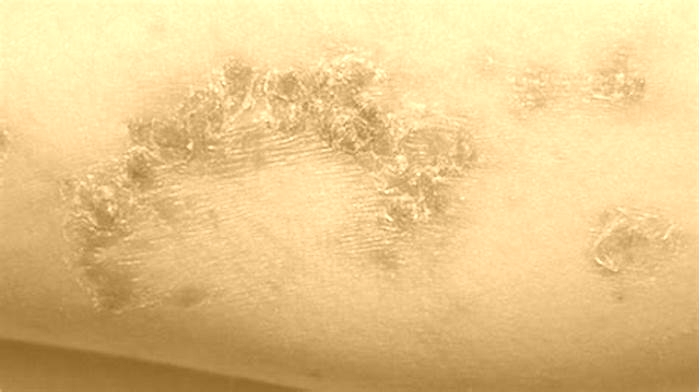
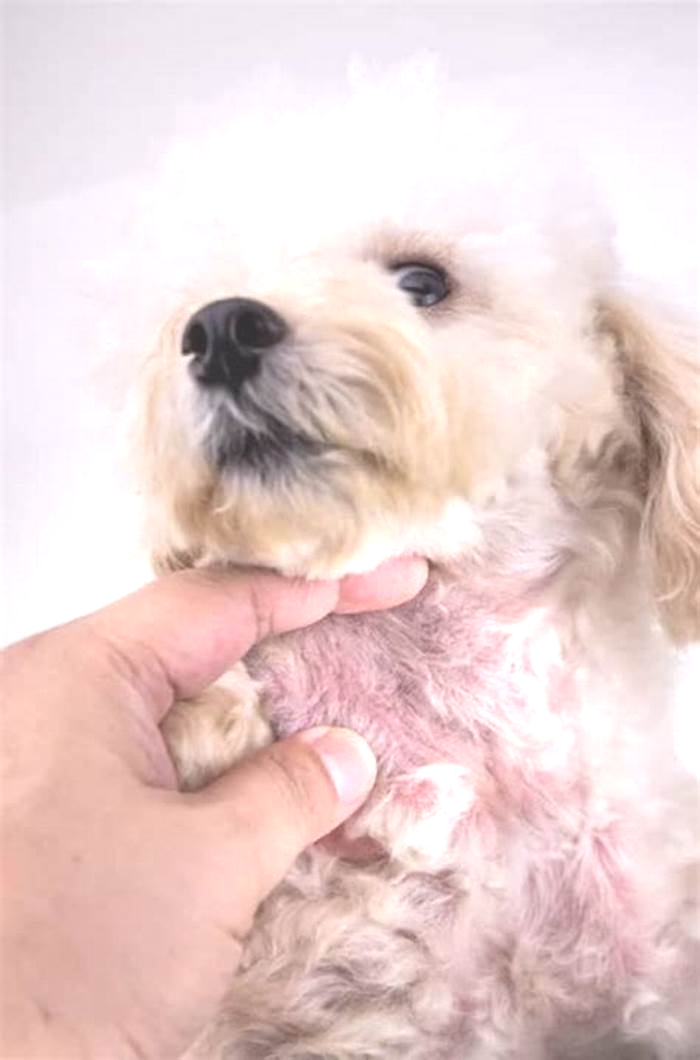
Can dog skin infection go away on its own
Pyoderma in Dogs
Pyoderma literally means pus in the skin. It can be caused by infection, inflammation, or cancer and is common in dogs.
Most cases of pyoderma are caused by bacterial infections. Most of these are superficial and secondary to a variety ofother conditions, such as allergies or parasites. Pyoderma that occurs in otherwise healthy animals usually resolves completely with appropriate antibiotics. Warm, moist areas on the skin, such as lip folds, facial folds, armpits, feet, and neck folds, often have higher bacterial counts than other areas and are at an increased risk for infection. Pressure points, such as elbows, are prone to infections due to repeated pressure. Any skin disease that changes the normally dry, desert-like environment to a more humid environment can cause overcolonization of the skin with bacteria.
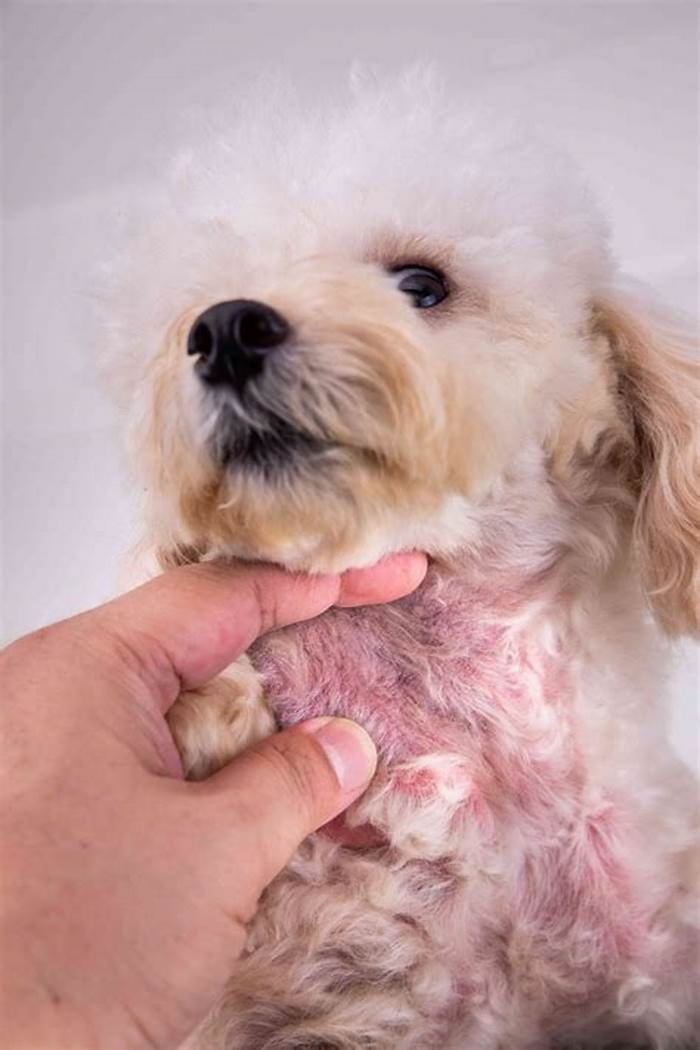
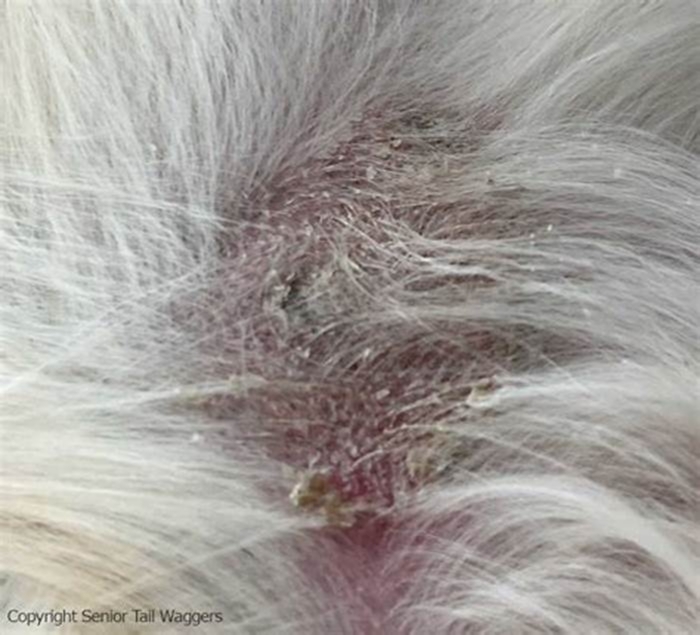
The most common sign of bacterial pyoderma is excessive scaling. Scales are often pierced by hairs. Itching is variable. In dogs, superficial pyoderma commonly appears as bald patches, welts around hairs, and scabbing. Shorthaired breeds often have multiple welts that look similar to hives because the inflammation in and around the follicles causes the hairs to stand more erect. These hairs are often easily removed, which distinguishes pyoderma from hives. Hair loss leads to small bald patches in affected areas. At the margins of the hair loss, there may be redness and welts but these signs are often absent in shorthaired breeds. The signs of deep pyoderma in dogs include pain, crusting, odor, and secretions of blood and pus. Redness, swelling, ulceration, scabs, and blisters may also be seen. The bridge of the muzzle, chin, elbows, hocks, knees, and spaces between the toes are more prone to deep infections, but any area may be involved.
Diagnosis is based on signs. Diagnosis of pyoderma must also include steps to identify any underlying causes. These include fleas, allergies, hypothyroidism, Cushing disease, and poor grooming. Multiple deep skin scrapings are needed to exclude parasitic infections. Bacterial and fungal cultures may also betaken.
The most common causes of recurrent bacterial pyoderma include failure to treat underlying causes, use of glucocorticoid drugs, and inappropriate treatment with prescribed antibiotic medications. You may contribute to a recurrence of pyoderma in your dog if you dont carefully follow your veterinarians treatment directions. Even though your dog may seem better after only a few days or a week, it is still very important for you to continue the prescribed treatment program for the full length of time. The bacteria causing pyoderma can still be present and ready to multiply again if the complete course of medication is not given.
Antibiotic treatment should last for at least 3 weeks and preferably for 4 weeks. All signs (except for hair regrowth and resolution of increased pigmentation) should be gone for at least 7 days before antibiotics are discontinued. Longterm, recurrent, or deep pyodermas typically require 8 to 12 weeks or longer to heal completely. Topical antibiotics may also be used in some cases.
Attention to grooming is crucial. The hair coat should be clipped in dogs with deep pyoderma and a professional grooming is recommended in medium to longhaired dogs with superficial pyoderma. This will remove excessive hair that can trap debris and bacteria and will help grooming.
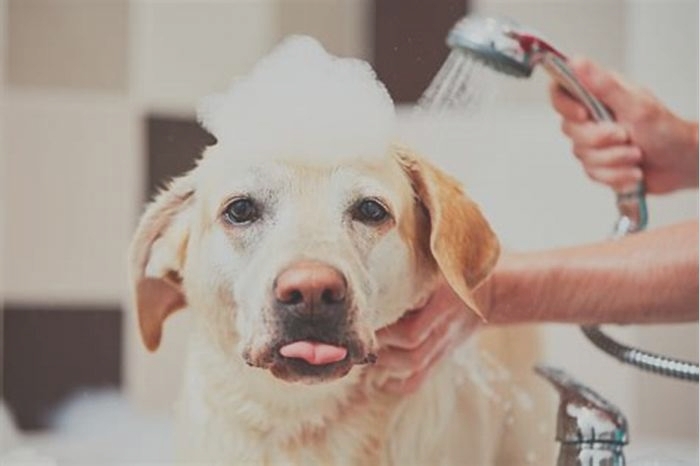
Dogs with superficial pyoderma should be bathed with a shampoo recommended by its veterinarian. Baths should be given 2 to 3 times per week during the first 2 weeks of treatment and then 1 to 2times per week until the infection clears. Dogs with deep pyoderma may require daily baths with medicated shampoos diluted to one-half or one-quarter strength. Shampooing will remove bacteria, crusts, and scales, and reduce itching, odor, and oiliness. Improvement may not be evident for at least 14 to 21 days, and recovery may not be as rapid as expected. Your veterinarian can recommend the appropriate bathing program for your pets condition. Medicated shampoos usually need to remain on the coat for 10 minutes in order to be effective.
Also see professional content regarding pyoderma.
Cellulitis Symptoms Not to Ignore
Cellulitis is a common skin infection with symptoms that may include an irritated or painful rash, skin blisters, swelling, and fever. Early treatment is the best way to prevent potentially serious complications from cellulitis.
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection. It happens when small cuts or other skin breaks allow bacteria to enter. It causes painful inflammation and swelling and can make your skin feel overly warm. In most cases, cellulitis outbreaks occur on the lower legs. However, your arms, face, and other areas of the body can also be affected.
Its important not to ignore cellulitis symptoms. The condition will not go away on its own, but early treatment can prevent serious complications. If cellulitis is left untreated, the infection can spread to the bloodstream and to the lymph nodes. Once the infection begins to spread, it can quickly become life threatening.
Cellulitis causes a range of painful and unpleasant symptoms. In most cases, symptoms only occur on one side of the body. Early treatment can prevent complications and stop the spread of cellulitis before it becomes life threatening.
Common cellulitis symptoms
The early symptoms of cellulitis can present differently in different people. The symptoms and how severe they are can also vary depending on the part of your body thats affected.
General symptoms of cellulitis typically include:
- blisters
- swelling
- an irritated rash
- lines that run outward from the main rash area
- pain in the affected area
- skin thats tender to the touch
- skin thats warm to the touch
- skin that feels tight or looks glossy
- skin dents or dimpling
- fever
- headache
Severe symptoms of cellulitis
Symptoms usually get more severe as cellulitis spreads. These symptoms are a sign the infection has spread to your bloodstream.
Symptoms of severe cellulitis include:
- a rash thats growing and changing rapidly
- a very large rash thats inflamed and painful
- numbness, tingling, or any other changes in sensation in the affected area
- skin darkening
- swelling and inflammation around your eyes or behind your ears
- lightheadedness
- fatigue
- chills
- weakness
- muscle aches
Its always important to see a doctor for cellulitis. This condition will not go away without medical care. Its best to make a medical appointment right away if you notice any symptoms that could be a sign of cellulitis.
Some symptoms indicate that cellulitis is spreading. Get immediate medical care if you:
- notice any symptoms of cellulitis and you also have diabetes
- have fever along with a painful rash that continues to grow and spread
- notice changes to how your skin looks or feels
- feel feverish, achy, fatigued, or lightheaded, and also have a painful rash
Symptoms of cellulitis will often get worse within the first 48 hours of receiving treatment. Youll usually start to see an improvement within 2 to 3 days of starting antibiotics. If your symptoms do not start to improve during this time, contact your doctor. You might need a different treatment.
Cellulitis is often diagnosed through physical examination. A doctor will examine your skin and may be able to make a diagnosis based on your rash and other skin symptoms. Sometimes bloodwork is ordered to rule out similar skin conditions and infections.
The most common
If your symptoms are severe or do not respond to antibiotics, you might need to be hospitalized. In the hospital, youll receive intravenous (IV) antibiotics. If you have any abscesses in your skin, they may need to be surgically drained.
Cellulitis can be successfully treated with antibiotics. However, untreated cellulitis can lead to serious complications and can even be fatal. Complications of cellulitis include:
- Bacteremia: Bacteremia is a potentially life threatening infection in your bloodstream that can spread quickly.
- Endocarditis: Endocarditis is a life threatening infection and inflammation of your heart.
- Sepsis: Sepsis is a medical emergency caused by your bodys response to a severe infection.
- Osteomyelitis: Osteomyelitis is a painful bone infection that often needs surgical treatment.
- Necrotizing fasciitis: Necrotizing fasciitis is a life threatening and painful infection of body tissues under the skin.
There are steps you can take to reduce the risk of cellulitis, especially if you have risk factors for developing the condition.
Some steps you can take to prevent cellulitis include:
- Always gently washing any wounds or cuts on your skin with soap and water.
- Using protective creams and other moisturizers like Vaseline to help keep bacteria out of cuts and wounds.
- Covering wounds and cuts with bandages and changing them at least once a day.
- Monitoring any cuts or wounds for signs of infection like pain, irritation, or pus.
- Moisturizing your skin daily to prevent cracks.
- Wearing gloves, socks, and other weather-appropriate clothing to prevent cold weather from damaging your skin.
- Wearing gloves for household chores and any time your hands might be exposed to chemicals.
- Always treating any skin infections, including common minor conditions like athletes foot, quickly.
- If you have a weakened immune system, talking with your doctor about extra precautions you can take to avoid cellulitis is helpful.
Cellulitis is a skin infection that can be easily treated with antibiotics.
However, it can be fatal without treatment. Untreated cellulitis can spread and quickly cause life threatening complications. Its important to seek medical care as soon as you notice any symptoms of cellulitis.
Early symptoms of cellulitis include an irritated and painful rash thats warm to the touch. Your skin might blister and swell, and you might develop a fever. More severe symptoms such as a growing and changing rash, a change to the appearance of or sensation in your skin, and lightheadedness are signs you need urgent medical care.
Good skin care can help you prevent cellulitis. Be careful to clean and cover any wounds and cuts and wear protective gloves when needed. Your doctor might have additional suggestions that are specific to your cellulitis risk factors.
How to know if a sinus infection is improving
As a sinus infection gets better, people will start noticing an improvement in symptoms.
A sinus infection can cause congestion, postnasal drip, and facial pressure. As the infection ends, symptoms will start resolving.
Most sinus infections develop due to a virus. However, bacterial infections can also cause some sinus infections.
Bacterial sinusitis can also develop when the nasal cavity and sinuses initially become inflamed due to a viral infection. When the fluid builds up in the sinuses, bacteria can grow, causing a bacterial sinus infection.
Antibiotics may be necessary to treat a bacterial sinus infection.
This article looks at the stages of a sinus infection, symptoms, how to tell if a sinus infection is going away, treatments, and when to contact a doctor.
People will know a sinus infection is getting better if they notice an improvement in their symptoms. This is the same whether or not they require antibiotics.
People may notice that the following symptoms begin to ease:
According to the
If a person requires antibiotics, they may need to take them for 328 days, depending on the type of antibiotic.
People may not notice an improvement in symptoms straight away, as the antibiotics will take time to fight off the bacterial infection. Once the antibiotics start taking effect, people should start to notice an improvement in symptoms.
If symptoms do not improve
If antibiotics are working to resolve symptoms, treatment can last 57 days in adults and 1014 days in children.
What happens at the end of a sinus infection?
Toward the end of a sinus infection, symptoms will improve and start going away. People may notice symptoms easing, such as less congestion, less postnatal drip, or easing pressure in the face.
According to the Allergy and Asthma Network, a sinus infection can last weeks, months, and in some cases, years.
A sinus infection can be acute, subacute, or chronic:
- Acute: Acute sinusitis lasts for 4 weeks or less and may resolve without medical treatment. Some people may require treatment and must contact a doctor if symptoms last longer than 710 days.
- Subacute: Subacute sinusitis lasts 48 weeks, and symptoms continue even with medical care.
- Chronic: Chronic sinusitis lasts for 8 weeks or longer. Symptoms will persist, and a doctor may need to check for underlying medical conditions.
According to the
- severe facial pain or headache
- symptoms that improve and then worsen
- symptoms lasting longer than 10 days with no improvement
- fever lasting for more than 34 days
- recurrent sinus infections over a year
In rare cases, a sinus infection can spread to other areas and become dangerous. People will need to seek immediate medical attention if they have any severe or concerning symptoms, including:
- neck stiffness
- severe headache
- change in vision
- fever that does not go away
A sinus infection can resolve without medical intervention, and people will often not require antibiotics. A sinus infection will usually resolve
Other medications for a sinus infection may help people manage symptoms. These medications include:
- Nasal decongestants: Topical nasal decongestants help reduce swelling in the nasal passages, which helps increase the flow of the blocked sinuses and allow drainage. It is important not to overuse nasal decongestants and only use them for 34 days, as prolonged use can worsen symptoms.
- Antihistamines: Antihistamines help reduce inflammation and fight symptoms of an allergic reaction, which may cause blocked sinuses.
- Combination drugs: Over-the-counter drugs may combine nasal decongestants and antihistamines. It is important to use these carefully, as some medications may thicken mucus and worsen the problem.
- Nasal corticosteroids: Nasal corticosteroids are topical prescription drugs. They are in the form of nasal sprays and help treat swelling and inflammation in the nasal passages and sinuses.
Home treatments
- placing a warm compress across the nose and forehead
- breathing in steam from a hot shower or bowl of hot water
- using nasal saline washes to rinse out thick nasal discharge
Antibiotic treatment
In some cases, people may require antibiotics if symptoms show no improvement in 10 days.
A doctor will only prescribe antibiotics if necessary. Before prescribing antibiotics, they may suggest waiting
If people require antibiotics, treatment
If symptoms do not improve after 7 days, a doctor may prescribe an antibiotic that targets a broader spectrum of bacteria, such as:
- amoxicillin-clavulanate, for 1014 days
- cefuroxime axetil
- cephalosporins
- clindamycin, by itself or with ciprofloxacin
- sulfamethoxazole
- fluoroquinolones
After 57 days with no improvement, a doctor may prescribe an additional antibiotic, such as metronidazole or clindamycin.
People may be able to tell they are recovering if symptoms start easing and going away.
Home treatments, over-the-counter medications, and prescription medications can help treat a sinus infection. In some cases, people may require antibiotics.