Does seborrhea go away on its own

Bookshelf
Introduction
Seborrheic dermatitis is a non-contagious skin condition. It leads to scaly patches of skin with oily, dandruff-like flakes, especially on your face and scalp. It is only rarely itchy. Experts believe that seborrheic dermatitis is made more likely by certain things. These include an increased production of sebum (an oily substance) in the skin, too much of a yeast (fungus) that lives on the skin, and a weakened immune system.
If someone first has the scaly rash as a teenager or adult, it almost always tends to come back again and again. Then it helps to apply antifungal medicines or steroid creams to the inflamed areas of skin.
The situation is very different in babies, though: If seborrheic dermatitis occurs during the first few months of a childs life, it usually goes away on its own within one year and also doesnt come back. This is commonly known as cradle cap.
At a glance
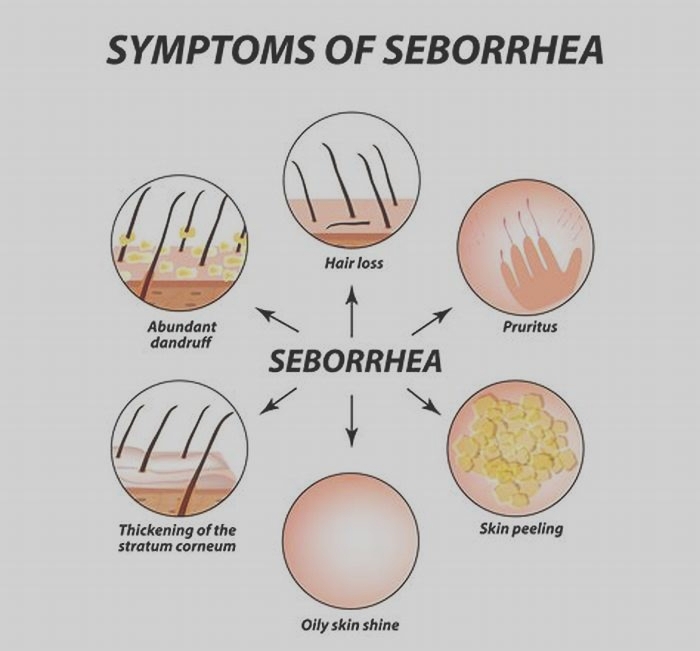
The typical symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis are scaly flakes of skin on your face and scalp.
This rash isn't contagious, but it does keep on coming back in adults.
Creams and shampoos can relieve the symptoms.
No treatment is needed in babies (where it is commonly known as cradle cap).
Symptoms
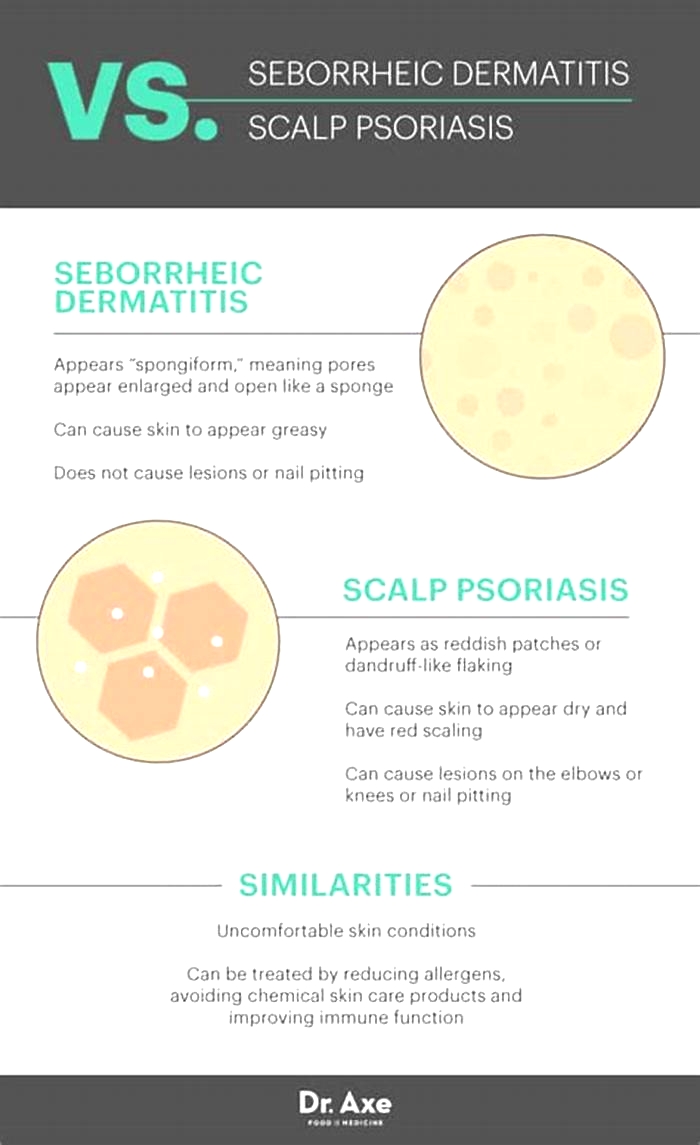
The typical symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis are patches of skin covered with yellowish, shiny, oily scales. On light-colored skin, these patches look reddish. On dark skin, the scaly areas look like lighter patches. They dont usually itch.
The patches occur most commonly on areas of skin that have a lot of sebaceous (oil-producing) glands. These typically include areas
along the hairline and on the part of the scalp covered with hair,
along and between the eyebrows,
on the cheeks and particularly in the folds of skin there that run from the nostrils down to the corners of the mouth.
The rash can also spread to other parts of the body, most commonly above the breastbone and on the back near the thoracic spine. Folds of skin may be affected too for example, under the breasts, or in the armpits or groin area. In men, the patches sometimes also occur in the genital area.
Seborrheic dermatitis: Typical areas and appearance on light and dark skin
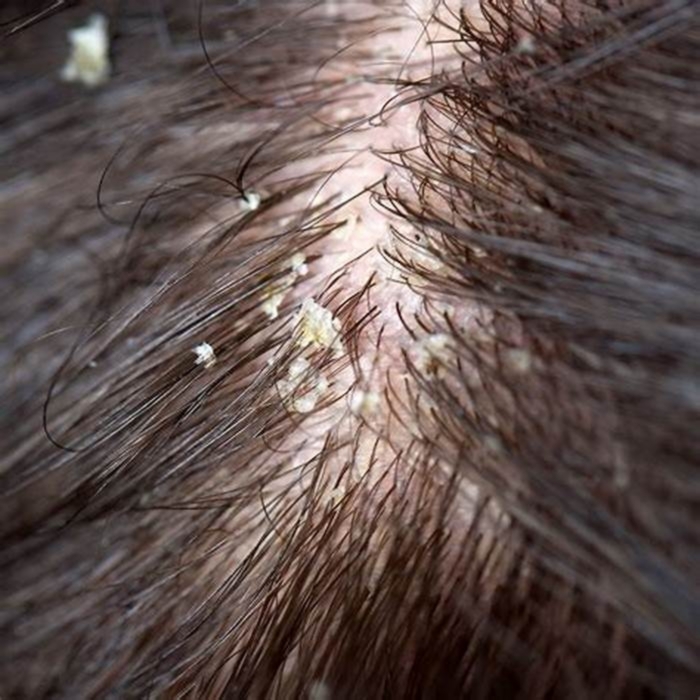
In babies, seborrheic dermatitis mostly affects the scalp.
Causes and risk factors
The scaly patches of skin are probably caused by various factors. These include an increased production of sebum (skin oil) and the usually harmless growth of a certain type of yeast (Malassezia furfur) on the skin.
Other factors that can play a role here include bacteria, stress, genes, hormones, nervous system disorders like Parkinsons disease, and a weakened immune system. People with a weakened immune system also have a higher risk of developing a more severe type of seborrheic dermatitis that spreads to the rest of the skin and is harder to treat.
Prevalence and outlook
Seborrheic dermatitis is common: About 3 to 10 out of 100 people are affected. It is more common in men than in women. People usually get the scaly rash for the first time either when they are young adults or over the age of 50.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic condition in adults and teenagers, with symptoms that vary in their severity over time. These skin symptoms might also go away for a while often in the summer. But they may return in the winter or during periods of stress.
Diagnosis
Seborrheic dermatitis is easy to diagnose if scaly, non-itchy, red or lighter patches of skin appear on typical parts of the body. Usually, its enough to have a detailed talk with the doctor and then a physical examination. The doctor will first try to rule out other skin conditions that are similar to seborrheic dermatitis, such as psoriasis or atopic dermatitis (also called atopic eczema or simply "eczema"). Like seborrheic dermatitis, these conditions cause changes in the skin, but usually on other parts of the body. In eczema, the inflamed skin is itchy. On light-colored skin, its made up of reddish patches without clearly defined edges, and sometimes small blisters too. On dark skin, the areas affected by eczema appear darker than the surrounding skin. And instead of blisters, small, firm bumps (papules) are more likely to develop.
Further examinations are only rarely needed. For instance, a swab test can be done and sent to a laboratory to find out whether its a bacterial skin infection such as impetigo. It is usually not necessary to take a sample of the tissue (biopsy).
Treatment
In teenagers and adults, the symptoms can be relieved by applying certain medications to the inflamed patches of skin. Medicines that can be used include:
It usually isnt necessary to take any pills or tablets. Because sunlight can make seborrheic dermatitis improve, some people also try phototherapy with UVB light.
There is no treatment that can clear up seborrheic dermatitis for good.
Babies don't usually need treatment for seborrheic dermatitis because it goes away on its own in babies.
Everyday life
Although seborrheic dermatitis is harmless, it can still be distressing for teenagers and adults: The scaly patches of skin often occur on the face, making them visible to others. And they may never go away again. If you feel very bad about your skin, you can talk with a doctor about finding a way to better cope with the condition, for instance with the help of behavioral therapy.
It is not a good idea to cover up the inflamed patches of skin with a heavy foundation or concealer because that clogs the pores in the skin. But its okay to use a light foundation every now and then. Mild, non-oily skin care products are well suited for skin care.
You dont need to use special sun protection for seborrheic dermatitis. Exposing the skin to sunlight and fresh air, for example by going to the beach, may even reduce the symptoms. It is enough to use an appropriate sunscreen strength for your skin type. Less oily sun lotions are more suitable than very oily lotions.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common form of eczema that usually affects the scalp, though it can affect other parts of the body as well.

While it rarely causes severe harm to the body, it can be uncomfortable to live with the constant itch, rash and other symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis. Fortunately, there are some effective treatment options and seborrheic dermatitis can sometimes go away on its own or with the right shampoo and skin care routine.
Lets dive into who gets seborrheic dermatitis, why it forms, common symptoms and treatment options.
What is seborrheic dermatitis?
Considered a chronic form of eczema, seborrheic dermatitis appears on the body where there are a lot of oil-producing (sebaceous) glands like the upper back, nose and scalp. It can cause a variety of symptoms from dandruff to a rash on the affected area.
For many infants and some adults, seborrheic dermatitis goes away on its own. If symptoms dont go away, there are many effective treatments to manage symptoms and stop seborrheic dermatitis flare-ups in the future.
Who gets seborrheic dermatitis and why?
Seborrheic dermatitis (also sometimes referred to as seborrhea or seborrhoeic dermatitis), can affect people of any age, though its most common in infants and adults between the ages of 30 and 60. Among adults and teens, this skin disease is more common in males.
In infants, this common skin condition usually clears on its own and doesnt come back. In adults, however, the prevalence of seborrheic dermatitis usually follows a pattern of flaring and clearing that can last for years.
Some research suggests 3-10 out of every 100 people will experience seborrheic dermatitis in their lifetime. Many folks who get seborrheic dermatitis as a young adult or after 50 suffer from chronic seborrheic dermatitis and they experience flare-ups throughout their life.
What causes seborrheic dermatitis?
Seborrheic dermatitis is usually caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
The trigger is usually an inflammatory reaction to excess Malassezia yeast, also sometimes called pityrosporum. This organism that normally lives on the skins surface, is the likely cause of seborrheic dermatitis. The Malessezia overgrows and the immune system seems to overreact to it, leading to a fungal infection that results in skin changes.
Certain medical conditions can increase peoples risk of developing seborrheic dermatitis, including psoriasis, HIV, acne, rosacea, Parkinsons disease, epilepsy, alcoholism, depression, eating disorders and recovery from a stroke or heart attack.
Common triggers for seborrheic dermatitis include:
- stress
- recovery from a stressful life event, like losing a loved one or a heart attack
- hormonal changes or illness
- harsh detergents, solvents, chemicals and soaps
- cold, dry weather or a change in the season
- some medications, including psoralen, interferon and lithium
- certain medical conditions, such as HIV and Parkinsons disease
Like all forms of eczema, seborrheic dermatitis is not contagious. You cannot catch it from another person. Instead, its the result of environmental and genetic factors.
What are the symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis?
Seborrheic dermatitis can be the culprit for a variety of symptoms depending on age, race, and the severity of a flare-up. Sometimes, symptoms will go away on their own or with changes in your skincare and hair regimens.
Seborrheic dermatitis and cradle cap in infants
Infants with seborrheic dermatitis most often have a form called cradle cap, which appears on their scalps as scaly, greasy patches. Infants can also develop seborrheic dermatitis on their bottoms, where it can be mistaken for diaper rash, a form of contact dermatitis.
Seborrheic dermatitis in adults and adolescents
When seborrheic dermatitis appears near the scalp in adults and adolescents, its often referred to as facial seborrheic dermatitis. Common symptoms of facial seborrheic dermatitis include inflamed skin and itching.
With this form, symptoms might also appear on the eyelids, on the sides of the nose, in and around the eyebrows and near the ears. Facial seborrheic dermatitis can also cause stubborn dandruff. But seborrheic dermatitis doesnt just form on the face. It can appear in oily skin all over the body. In addition to the face, redness, swelling and greasy scaling can develop on the mid-chest, upper back and in the armpits, under the breasts and in the groin area.
Common symptoms
No matter where seborrheic dermatitis is on the body, there are common symptoms experienced by many with this condition. These symptoms include:
- Flaking skin or dandruff;
- Patchy of flaky white or yellow scales on top of greasy skin;
- A irritable rash which looks dark in brown and Black skin and lighter in white skin;
- Ring-shaped rash for those with petaloid seborrheic dermatitis;
- Itchiness.
The affected skin sometimes crusts over and lesions containing sebum can form. Erythema, or redness of the skin caused by inflammation, may also be experienced. If the flare-ups occur in creases in the hairline, those who itch the affected areas too much may experience hair loss as well.
African Americans and those with skin of color might experience petaloid seborrheic dermatitis, a more severe form where lesions form around the hairline and skin discoloration happens. Usually, the discolored skin manifests in a ring-shaped rash. When looking more generally at the relationship between eczema and skin of color, itching due to eczema has been shown to have a greater impact in Black patients, who are also more likely to have severe disease.
Symptoms of severe cases
More severe cases can lead to the immunodeficiency of affected skin and an increased risk for infections. Seborrheic dermatitis is not precancerous. If you have this form of eczema, it does not increase your chance of getting skin cancer.
Another common misconception is that seborrheic dermatitis leads to hair loss. This is completely false. Hair loss is not a symptom of seborrheic dermatitis and if you are experiencing hair loss, you probably have a different underlying condition.
Whether your severe symptoms are from seborrheic dermatitis or something else, its best to visit an experienced healthcare provider, such as a dermatologist. This healthcare provider can help you get your severe symptoms under control so they stop disrupting your daily life.
How is seborrheic dermatitis treated?
Depending on the severity of the case, you might be able to treat this form of eczema with a shampoo swapor seborrheic dermatitis might even go away without treatment. If symptoms persist for longer than two weeks, you probably want to consider talking to a healthcare provider about over the counter and prescribed treatment options. Most adults with this condition will need a treatment plan to manage symptoms.
Use the right shampoo and skincare products
Following a skincare routine can help keep symptoms under control. Wash affected areas daily with a gentle, zinc-containing cleanser (2% zinc pyrithione) and follow up with a lotion or moisturizer.
If the hairline is affected, consider a dandruff shampoo and hair products designed for sensitive skin. Some of the best non prescription dandruff shampoos include those with:
- Pyrithione zinc. Selenium sulfide;
- Ketoconazole 1%;
- Tar;
- Salicylic acid.
Popular brands with one or more of these active ingredients include DermaZinc, Head & Shoulders, Selsun Blue, Nizoral and Denorex Extra Strength.
For more on the best products for infants with cradle cap, adolescents, and adults with seborrheic dermatitis, check out our list of products with the NEA Seal of AcceptanceTM.
Lifestyle changes
Healthy lifestyle habits, like managing stress and getting plenty of sleep, can also improve skin. Stress relief is often the lifestyle change which will have the biggest impact on seborrheic dermatitis. Some particularly effective stress relief techniques include:
- Perform light exercise, such as yoga or a gentle walk;
- Journal about stress and negative feelings;
- Develop a mediation or breathwork practice;
- Spend time in nature, even if its just five minutes.
There are many other ways you can reduce stress. What matters most is finding an enjoyable technique that allows you to slow down and devote time to self care.
Over the counter treatments and medicated shampoo
If lifestyle and skin care routine changes dont work, it might be time to consider over the counter (OTC) and prescription options. OTC and prescription treatment for this skin disorder is aimed at removing scales, reducing itch and calming the inflammation thats causing redness and swelling.
In infants, using an emollient such as mineral oil or petroleum jelly, to gently loosen scales is usually all thats needed. Care can be more complicated for adults, who often need ongoing treatment and self-care to help prevent flare-ups.
Dermatologists usually begin treating mild cases with a topical antifungal cream or medicated shampoo, such as a prescription anti-fungal shampoo or over-the-counter dandruff product.Some popular topical treatments include creams with 1% ciclopirox or 2% ketoconazole. Because both ciclopirox and ketoconazole can dry out the skin, its important to use a gentle moisturizer after applying a cream with either ingredient.
Prescribed treatments
If the condition is more severe, intermittent use of a topical corticosteroid like fluocinolone, dermatol, additional steroids or calcineurin inhibitor may be required. Other treatments for severe cases include hydrocortisone ointments or oral medications, such as pimecrolimusor tacrolimus.
Make sure to talk to a dermatologist or another healthcare provider who is experienced in dermatology about options for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis and the side effects of each option.
When to see a healthcare provider
If youre considering over the counter or prescription options, you will want to discuss the best path with a doctor. It might also be a good idea to discuss any lifestyle changes or skin and hair products with a healthcare provider before taking them.
You should also see your healthcare provider if you experience a severe flare-up or have worse symptoms than usual. In this case, your doctor can help you change your medication dose or switch to a different treatment option.
After talking to your healthcare provider, they may order a skin biopsy. This is when a small piece of your skin is removed in order to be studied in a lab. The skin biopsy can help your healthcare provider determine if this is seborrheic dermatitis or something else and the best treatment plan moving forward.
Whether they order a skin biopsy or not, it will most likely be useful to discuss your seborrheic dermatitis with your doctor. During an appointment, your healthcare provider might ask you:
- How long have you had symptoms? What are your current and past symptoms?
- What treatment options have you tried and how have they worked?
- What treatment options are covered by my insurance?
- How often should we meet to monitor my seborrheic dermatitis?
After your healthcare provider gathers the answers to these questions, examines the affected areas, and possibly orders a skin biopsy, they should have customized recommendations on how to create a treatment plan moving forward.
What do the ecz-perts have to say?
Seborrheic dermatitis isnt contagious and is not an allergy, although some allergies can mimic it, said Dr. Peter Lio, clinical assistant professor of dermatology and pediatrics at Northwestern Universitys Feinberg School of Medicine. A correct diagnosis, he added, requires careful evaluation by a dermatologist.
Seborrheic dermatitis can also overlap with atopic dermatitis, especially in infants. We see this overlap in young adults, as well, usually in those with more severe atopic dermatitis, Lio said. They can develop a condition that some call head and neck dermatitis that seems to be very closely related to seborrheic dermatitis and is treated similarly.
In conclusion
If you are experiencing seborrheic dermatitis, theres no need to fret. While the symptoms can be irritating, there are many effective treatment options out there. After a conversation with a healthcare professional, you should be able to develop a treatment plan for even the most severe case.