How do I know if it s eczema or fungus
How to tell whether you have athletes foot or eczema
Eczema on the feet and athletes foot can both cause itching and skin inflammation. However, eczema is typically more widespread and affects larger joints, whereas Athletes foot is often localized to the toes.
Despite their similar symptoms, the two conditions are unrelated. Environmental and genetic factors contribute to eczema, while athletes foot results from a fungal infection.
This article reviews the differences between athletes foot and eczema, including causes, treatments, outlook, and more.
Eczema and athletes foot both affect the skin and can cause itchy, red, and inflamed patches. However, they are two distinct conditions with different causes, typical locations, and treatments.
One of the main differences is the underlying cause. Athletes foot
Athletes foot tends to affect the toes and feet. Eczema typically affects the joints, such as the elbows and knees, but it can affect other areas too.
With treatment, athletes foot should go away on its own, though a person can have subsequent infections. Eczema will typically require long-term management to help prevent flare-ups.
The table below outlines the differences between athletes foot and eczema:
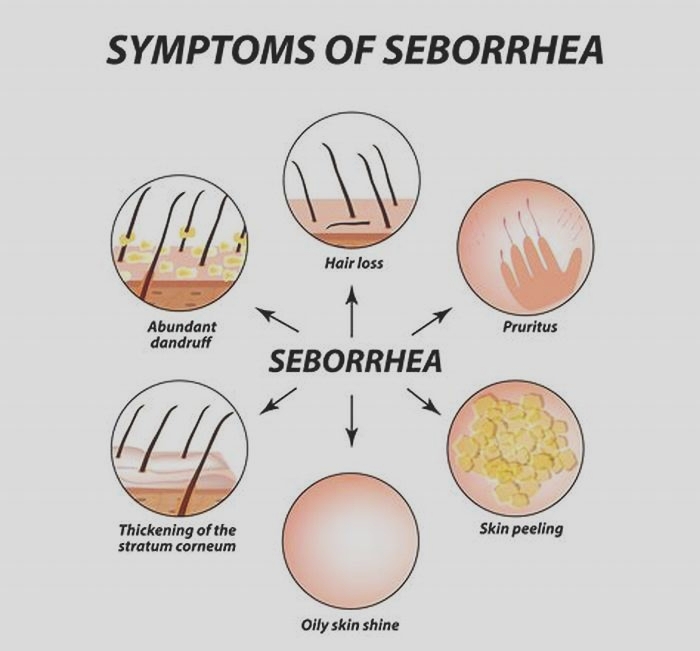
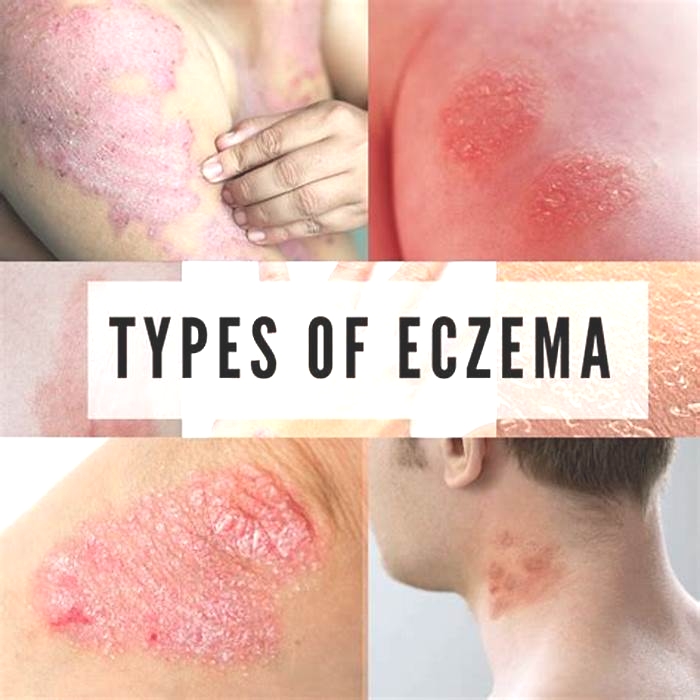
Eczema is an inflammatory skin condition associated with dry, itchy patches of skin. There are seven types of eczema. The most common is atopic dermatitis, which leads people to use the terms interchangeably.
More than 31 million people in the United States have some form of eczema, reports the National Eczema Association. It can develop at any time from childhood through adulthood.
People often associate eczema with flare-ups, or flares. Flares are periods of time, lasting for several days to several weeks, when symptoms worsen. With proper treatment and management, a person can help reduce the occurrence and severity of flares.
Learn more about eczema here.
Eczema symptoms
Eczema symptoms can vary between people. One persons eczema may look different from anothers, and it can even look different in different areas of a persons body.
The most common eczema symptom is itchiness. Other common skin symptoms include:
- dryness
- rough, scaly, or tough patches
- sensitive skin
- inflamed, discolored skin
- swelling in different areas
- oozing or crusting
A person may have one, some, or all of the symptoms associated with eczema. Symptoms can occur anywhere but often occur around the joints, such as the elbows and knees.
What causes eczema?
The exact cause of eczema is unknown. However, experts believe several factors can contribute to its development, including a persons environment and genetics.
Environmental causes include contact with certain irritants or allergens that cause skin inflammation. Examples include:
- chemicals
- fragrances
- dyes
- food
- pet dander
Genetically, a person may have a filaggrin deficiency. This protein helps maintain moisture in the skin.
Learn more about eczema and genetics here.
How to manage eczema
Treatment and management may depend on the eczemas severity and its cause.
A doctor may recommend medications for moderate to severe cases, such as:
For milder cases, a person may be able to use creams and ointments that provide additional moisture to the skin, such as petroleum jelly.
A person should also try to avoid known triggers whenever possible. This can help prevent flares. A person can work with an allergist or another doctor to help determine their triggers.
Learn about natural remedies for eczema here.
Athletes foot is a fungal infection transmitted through direct or indirect contact with people who have the infection. A person can take steps to prevent infection by keeping their feet clean and dry and wearing footwear in moist or damp public areas, such as locker rooms.
Athletes foot causes an itchy, red rash that often forms around the toes and on the feet. Treatment typically involves topical or oral antifungal medications.
Athletes foot symptoms
Athletes foot causes fissures or scales on the skin that are often itchy and red. They typically occur between the toes but can also occur on the feet.
What causes athletes foot?
Athletes foot is a fungal infection. Dermatophyte fungi cause it. These fungi feed on keratin. The infection can recur, which means a person must continue to take steps to prevent infection.
Learn more about foot fungi here.
How to manage athletes foot
A person should take steps to prevent athletes foot by keeping their feet dry and wearing footwear in moist public areas. If an infection develops, doctors will likely recommend a topical or oral antifungal medication.
Learn more about athletes foot here.
People can take steps to prevent athletes foot infections and avoid eczema triggers. The following sections outline how.
Preventing athletes foot
To help prevent athletes foot, people can:
- avoid walking barefoot in public, moist areas, such as pools, saunas, or locker rooms
- wash feet every day with soap and dry them completely
- alternate shoes daily and avoid using wet or moist shoes
- keep feet dry
- not share shoes, socks, towels, or other linens with someone who has athletes foot
Preventing eczema
A person may not be able to prevent eczema entirely since genetics and environmental factors play a role. However, a person can take steps to avoid triggers and prevent flares, such as:
- reducing and managing stress with stress reduction strategies
- preventing dry skin by applying emollient moisturizers safe for eczema-prone skin
- avoiding irritants, such as pollen, pet dander, harsh chemicals, soaps, dyes, perfumes, and other substances when possible
A person may also wish to consider trying to understand their triggers and adapting their routines to reduce flares. For example, the effects of dry air on the skin in winter may require a different routine to that in the summer to help keep the skin moist.
A person may wish to contact a doctor if they develop an unfamiliar or severe rash that does not respond to treatment or does not go away after a few days. A doctor can help diagnose and treat the rash.
While some people with eczema find it improves as they get older, regular flares are common. However, avoiding triggers and adopting a good skin care routine can help people manage the condition.
Athletes foot should clear with antifungal treatment. Reinfection is possible, so people will need to take precautions to help reduce the likelihood.
Athletes foot and eczema both cause itchy, red, inflamed skin. Athletes foot is a fungal infection, while eczema is likely to have genetic or environmental causes.
Athletes foot typically occurs on the feet and toes, while eczema is more widespread. Eczema often occurs around the elbows and knees but may appear anywhere on the body.
Eczema is not contagious, but athletes foot is contagious. People can develop athletes foot when their skin comes in contact with the fungi that cause it. People may wish to avoid walking barefoot in moist public places to prevent infection.
Treatments for the two conditions also differ. Athletes foot requires fungal creams. Eczema often clears with topical steroids and moisturizers.
People can eradicate an athletes foot infection, but people with eczema are likely to have recurrent periods of flares and remission.
Is It Athletes Foot or Eczema? Here's How to Know
Itchy feet? Although you may chalk it up to plain old restlessness, it could also be athletes foot or eczema.
These two conditions are distinct, but people often confuse them because of their similar symptoms.
This article distinguishes between athletes foot and eczema and provides you with tips to prevent and manage each condition.
Athletes foot, also known as
The infection is contagious and can spread through direct skin contact or contact with skin flakes. It can enter through open skin, cracks, or wounds, and it thrives in moist and warm environments.
Thats why this infection commonly occurs on feet. For example, people commonly contract the infection through standing in communal showers.
On the other hand, eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that can affect quality of life and lead to infection if not properly treated. It can occur on any part of your body, including your feet. It is not contagious.
Eczema
Athletes foot and eczema have many similarities.
Both can cause skin redness, dryness, itchiness, and cracking. The affected skin may also thicken, swell, and turn white.
A
When you have eczema, infected skin
Athletes foot is often diagnosed via a physical examination, though some healthcare professionals
To diagnose eczema, a healthcare professional will typically take a careful history and perform a physical exam. They may also perform a skip biopsy. Since allergies are common with eczema, healthcare professionals
If you have athletes foot, a healthcare professional
You can help reduce fungal growth by washing and drying your feet regularly. Its also helpful to wear socks made with natural fabrics or quick-drying fabrics to minimize moisture. Avoid wearing tight shoes and, if possible, alternate the shoes you wear each day.
To prevent spread, be diligent about wearing flip-flops in public pools and changing rooms and avoid sharing towels, linens, or shoes with others.
If youre dealing with an eczema flare-up, you may find symptom relief through using OTC creams and shampoos that reduce redness and itching. Its also important to avoid harsh soaps.
Avoid wearing rough or non-breathable fabrics and try to avoid scratching as best you can. You may use
A healthcare professional
Because eczema is an inflammatory skin condition, eating more
Other lifestyle habits may also be beneficial in managing flare-ups. Drink lots of water and moisturize with fragrance-free products to keep your skin hydrated.
Its important to wash your feet regularly with soap and water. This can help prevent athletes foot in particular.
Additionally, you can help
- drying your feet with a clean towel after taking a shower or bath or swimming
- wearing flip-flops or slippers around public swimming pools, changing rooms, and showers
- avoiding very tight-fitting shoes
- taking your shoes off as often as possible
- wearing natural fabrics or fabrics that dry quickly
- washing your socks, bedding, and towels regularly at 140F (60C) or more
The following strategies may help minimize eczema flare-ups:
- Identify and avoid allergens and triggers.
- Moisturize your skin daily.
- Wear cotton clothing and avoid tight-fitting clothes.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Look for healthy ways to manage stress.
- Use a humidifier.
- Wash your laundry with unscented detergent.
- Avoid excessively hot baths and showers.
- Avoid sudden changes in temperature.
Learn more about preventing eczema flare-ups, especially during the summer.
Here are questions people often ask about athletes foot and eczema.
Can eczema be mistaken for athletes foot?
Yes, eczema can be mistaken for athletes foot since the symptoms can be similar.
If you suspect you have either condition, make careful note of your symptoms, lifestyle, and environment to discuss with a healthcare professional such as a podiatrist or dermatologist.
Can I use eczema cream on athletes foot?
No, eczema cream will not be effective to treat the fungal infection that causes athletes foot. You will likely need an OTC or prescription antifungal medication to treat athletes foot.
Is athletes foot the same as eczema?
No. Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin condition, while athletes foot is a fungal infection of the skin.
Although athletes foot and eczema can both affect the skin of the feet, they are two very different conditions.
Athletes foot is a fungal infection that can be transmitted through direct skin contact or contact with skin flakes, often in public pools and changing rooms.
Eczema is not contagious and is the result of genetic and environmental factors.
Both conditions can cause skin redness, cracks, lightening, and thickening, as well as itchiness and blisters that may weep.
Regardless of which one you have, its important to practice proper hygiene. Wash and dry your feet thoroughly, wear natural or quick-drying fabrics, and do laundry regularly. Consider wearing flip-flops in public spaces such as changing rooms.
Its also important to stay hydrated, eat a varied diet, and avoid any known inflammatory triggers.