How do I know if my groin rash is fungal
Tinea Cruris Treatment | Causes, Symptoms & Prevention
Tinea cruris, commonly known as jock itch, is a skin condition caused by a fungus. It's part of the tinea group of superficial fungal skin infections. Jock itch, like other tinea infections, is caused by dermatophytes, which are mold-like fungi. These fungi can affect the skin, hair, and nails.
Tinea cruris is usually harmless, but if it is allowed to thrive in warm, damp environments, it can quickly multiply and cause infection. Because of this, jock itch most commonly affects the skin around the groin, inner thighs, buttocks, axilla and inframammary area in women.
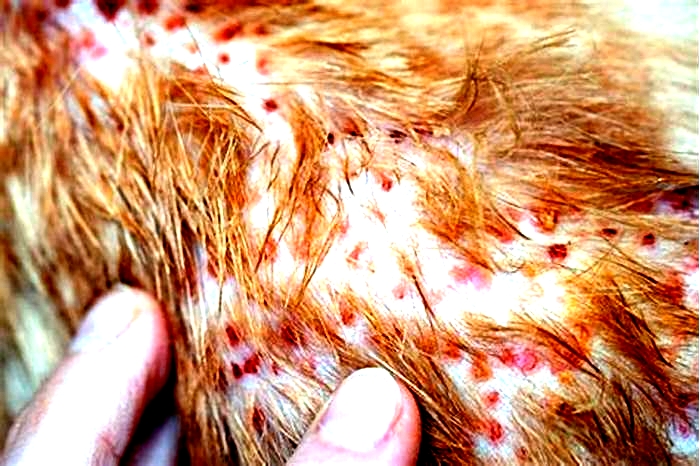
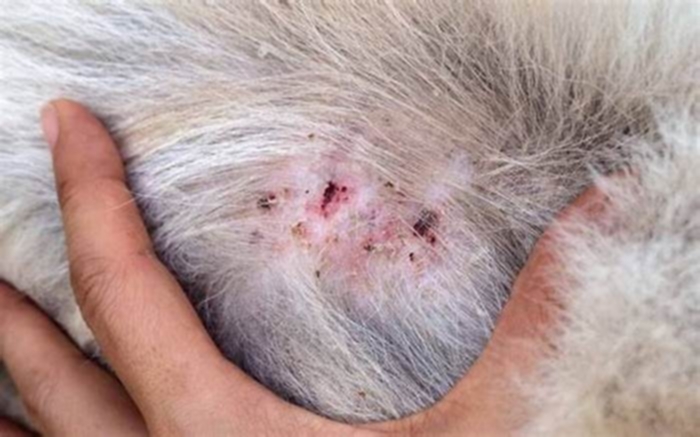
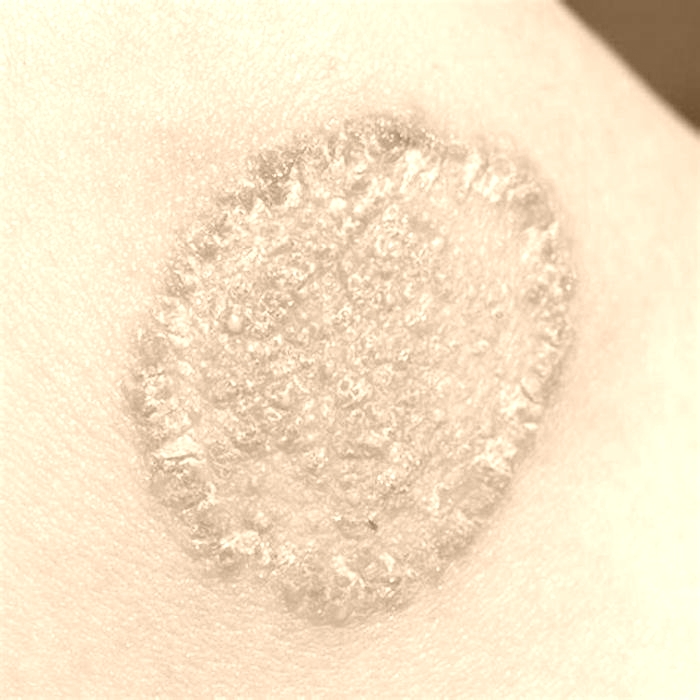
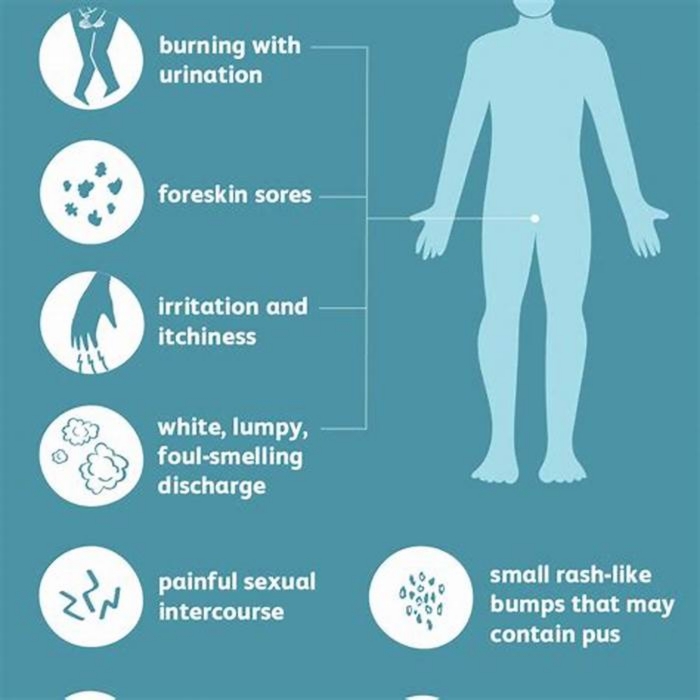
Men and adolescent boys are the most susceptible to jock itch. The infection results in a rash that itches or burns frequently. Tinea cruris usually presents as a dry, scaly, well-defined skin rash or a collection of small, pinpoint red or pink bumps. Because of its well-defined red border and central clearing, this type of eruption is commonly referred to as a ringworm.
Although jock itch might be uncomfortable, it is usually a minor infection. Treatment as soon as possible will reduce symptoms and prevent the rash from spreading. The majority of people can get relief just by using antifungal topical drugs and keeping the affected region clean and dry. Tinea cruris treatment may involve antifungal creams and, in rare cases, oral antifungal medicines.
For the majority of cases, Tinea cruris treatment is available. Long-term cases of jock itch are very rare and may be resistant to conventional drugs. These more resistant instances can often be managed with the right treatment and medication after due evaluation. Antifungal creams and, in rare cases, oral antifungal drugs may be used to treat jock itch caused by fungus. Proper groin hygiene, keeping the groin area clean and dry, and washing frequently with gentle soap and water are all part of the prevention and treatment for jock itch (especially after sweating or exercising).
Although the majority of cases of Tinea cruris are not contagious, infections can spread by physical or sexual contact, sharing swimsuits, or sharing towels. Through close skin contact, it is possible to spread fungal jock itch to others. Because of their overall health, activities, possible compromised immune state, exposure history, and other predisposing skin diseases like eczema, some people are simply more prone to acquiring jock itch. Tinea cruris may also be seen in people who have coexisting athlete's foot (tinea pedis).
What Causes Groin Rash?
There are many possible causes of a rash in your groin. It can be the result of something simple like heat and sweat, or something more complicated like bacteria or a parasite. Many causes of groin rash are treatable, and some are even preventable.
Jock itch is a fungal infection due to a fungus commonly found in gyms and locker rooms. It typically appears in your groin area. However, you can also find it in other areas like:
- upper thighs
- scrotum
- penis
- anus
Jock itch is not serious. The itching it causes can become very uncomfortable and even painful, however.
The symptom of jock itch is a rash that involves:
- itchiness
- raised and scaly edges
- redness or discoloration
- areas of oozing
- reddish-brown center
Jock itch is due to exposure to a fungus. This can happen through:
- skin-to-skin contact
- infected clothing
- damp towels
- public shower facilities
- locker rooms
Molluscum contagiosum is an infection resulting from a type of pox virus. This infection typically causes a mild, benign skin condition. It appears as lesions anywhere on your body, including:
- genital area
- face
- neck
- arms
- legs
- abdomen
Molluscum contagiosum typically clears on its own within
The lesions from molluscum contagiosum typically look:
- small and raised
- white, pink, or skin-colored
- dimply or pitted in the middle
- pearly
- smooth and firm
These lesions may also become:
- itchy
- red or discolored
- swollen
- sore
Heat rash is a common and harmless rash. It is typically very itchy. Heat rash appears in areas that tend to collect moisture when you sweat, such as:
- groin
- underarm
- under the breasts
- chest
- back
- elbow creases
- behind the knee
- waist
Heat rash is more common when you sweat more, such as in the summer or in hotter climates.
The symptoms of heat rash typically last from 23 days, and include:
- small red or discolored spots, or clear blisters
- itchiness
- sensation of prickliness
- redness or discoloration
- swollen areas
Intertrigo is a rash that typically appears in the folds of your skin. It is common in areas where the skin rubs together and holds moisture.
Intertrigo is most common in people who have:
- overweight
- diabetes
- weakened immune systems
- decreased mobility
- bowel or bladder incontinence
Intertrigo rash typically appears red, reddish-brown, or discolored. It may itch or burn. In some cases, the rash can ooze and have a foul smell. It may also crack and bleed, depending on the area it is in. While intertrigo can appear anywhere on your body, it is most common in these areas:
- groin
- armpits
- underneath breasts or belly
- creases of the neck
- between the buttocks
Learn more about skin conditions here.
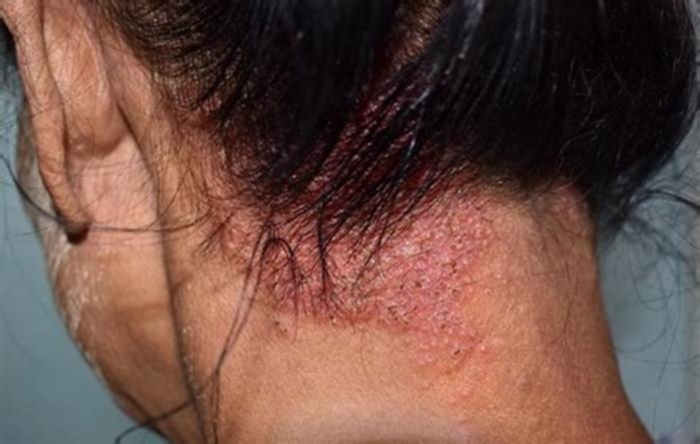
Erythrasma is a common skin condition that typically affects the folds of the skin. The most common areas to find it are:
- groin
- armpits
- between the toes
Erythrasma is the result of a bacteria called Corynebacterium minutissimum.It can affect anyone. However, it tends to occur more frequently in People of Color or when people experience:
The rash associated with erythrasma typically presents with:
- pink, brown, or discolored patches that are well-defined
- fine scaling
- superficial fissures
- itchiness
Other causes of groin rash
There are various other reasons you may develop a groin rash. These other causes include:
How do you treat groin rash?
Treatment for groin rash depends on the underlying cause of it. Some common treatments for causes of groin rash include:
- antibiotics, both oral and topical
- antiseptic cream
- emollient moisturizers
- antifungal cream
- steroid creams
Some causes of groin rash are self-limiting and do not require treatment. If you notice a rash in your groin area, contact your doctor so they can diagnose the cause and recommend the most effective treatment.
Read about when to see a doctor for a rash.
How can I prevent groin rash?
Many of the causes of groin rash are preventable. To help prevent groin rash, try these tips:
- Only use mild soaps.
- Avoid using products with fragrance.
- Change your underwear daily.
- Wear clean clothes and remove wet clothes right away.
- Maintain a moderate weight.
- Practice proper hygiene habits.
- Avoid sharing gym clothes, equipment, or towels.
- Use a condom or another barrier method when you have sex to prevent STIs.
There are many possible causes of a rash in your groin area. Most of these causes are treatable, and many are preventable.
If you develop a new and unexpected rash in your groin, contact your doctor. You might be able to treat it with over-the-counter products. However, it is important for your doctor to diagnose the underlying cause of the rash to recommend the most effective treatment.
With any kind of rash, avoid scratching it as this can lead to infection. If you notice symptoms of infection like pus, skin feeling hot to the touch, and inflammation in the area, contact your doctor right away.
Is It a Rash or Is It Herpes?
Herpes
If you have wet looking fluid-filled blisters in the vicinity of your mouth or genitals, chances are youve been infected with the herpes virus. When popped, the sores will crust over.
There are two types of herpes:
Although many people with the herpes virus never experience noticeable symptoms, the most common symptoms include:
Rashes
A rash is an inflammation of the skin caused by a number of factors ranging from skin irritants to sickness. Rashes are commonly identified by symptoms including:
The symptoms of specific rashes are typically different from herpes, even though they might appear in similar areas of the body. Common conditions that may cause a skin rash include:
Dermatitis
Dermatitis is a skin condition that causes red, itchy, flaky skin. There are two types of dermatitis: contact and atopic.
Contact dermatitis is a rash that appears after your skin touches an irritant, such as a perfume or chemical. Youll notice a rash appear where you touched the irritant, and blisters may also possibly form. A rash after exposure to poison ivy is one example of contact dermatitis.
Atopic dermatitis is also known as eczema. Its a rash that occurs after exposure to an allergen. Symptoms include thick, scaly, red patches of skin across the body.
Unlike herpes, dermatitis can occur anywhere on the body. Contact dermatitis will likely go away after exposure to the irritant has stopped and the skin is cleaned with a mild soap. Atopic dermatitis can be prevented by moisturizing the skin and avoiding triggers like hot showers and cold weather.
Shingles
Shingles is a painful skin rash that is believed to be caused by the same virus that causes chicken pox the varicella-zoster virus. Although shingles symptoms often include itching, fluid-filled blisters like herpes, the blisters usually appear in a band or in a small area on one side of a persons face, neck, or body along with an angry rash.
- Treatment for shingles. There is no cure for shingles, but there are antiviral drugs such as Acyclovir (Zovirax) or Valacyclovir (Valtrex) that your doctor may prescribe to shorten healing time and reduce your risk for complications. Your doctor may also prescribe pain medication such as the topical numbing agent, lidocaine.
Jock itch
Jock itch is a fungal infection that typically looks like a red rash with a few small blisters near the edge of the rash. Unlike herpes, these blisters typically do not crust over. Also, herpes blisters often appear on the penis, while the rash associated with jock itch typically appears on the inner thighs and groin, but not the penis.
Scabies
Scabies is a highly contagious skin infection caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite that burrows into your skin to lay eggs. While herpes is typically found in the mouth and genital area, scabies can be found anywhere on the body. A scabies infestation appears as redness or a rash, sometimes showing signs of small pimples, bumps, or blisters. Sores may appear when the area is scratched.
- Treatment for scabies.Your doctor will most likely prescribe a scabicide topical lotion or cream to kill the scabies mites and their eggs.
Genital warts
Resulting from infection from the human papillomavirus, genital warts are typically flesh-colored bumps that resemble cauliflower tops as opposed to the blisters caused by herpes.
- Treatment for genital warts.Along with prescription topical medications, your doctor might suggest cryotherapy (freezing) or laser treatment to remove the warts. There is no cure for the human papillomavirus, so no treatment is guaranteed to remove the warts and keep them from coming back.
Razor burn
Shaving your pubic hair can often create skin irritation and ingrown hairs, resulting in red bumps that can be mistaken for herpes sores. Razor burn is an acne-like rash. Ingrown hairs look like pimples with a yellow center, while herpes sores look more like fluid-filled blisters with clear liquid.
- Treatment for razor burn. There are a number of ways people address razor burns, ranging from over-the-counter topical creams with hydrocortisone to home remedies such as the topical application of witch hazel or tea tree oil.
Shop for hydrocortisone.
Shop for witch hazel.
Shop for tea tree oil.
Everything You Need to Know About Jock Itch
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Heres our process.
Healthline only shows you brands and products that we stand behind.
Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site. To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we:- Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm?
- Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence?
- Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices?
Jock itch is a fungal infection that can cause redness and itching of the groin or inner thighs. Home remedies and prescription medications can help ease symptoms and prevent the infection from spreading.
Tinea cruris, most commonly known as jock itch, is a fungal infection of the skin.
It belongs to a group of fungal skin infections called tinea. As in other tinea infections, mold-like fungi known as dermatophytes cause jock itch. These microscopic fungi live on your skin, hair, and nails.
Theyre typically harmless, but they can multiply quickly and cause infections when theyre allowed to thrive in warm, moist areas. Thats why jock itch usually develops in the skin around the groin, inner thighs, and buttocks.
Jock itch is most common in people assigned male at birth, particularly adolescents. The infection causes a rash that often itches or burns. On light skin, the affected areas can also appear red, flaky, or scaly. On darker skin, the rash might appear gray or brown.
Though jock itch can be bothersome, its typically a mild infection. Treating it quickly will minimize symptoms and keep it from spreading.
Most people find relief simply by applying topical antifungal medications and by keeping the affected area clean and dry.
Home remedies for jock itch
In most cases, you can treat jock itch using several at-home products. You can try the following remedies to get rid of the infection:
- Apply an over-the-counter (OTC) antifungal cream, powder, or spray to the affected area.
- Wash the affected area thoroughly with soap and warm water.
- Dry the affected area thoroughly after bathing and exercise.
- Change clothes and undergarments every day.
- Wear loose cotton clothing.
- Treat any other fungal infections, such as athletes foot.
Prescribed treatments for jock itch
If you take OTC medications or use home remedies for jock itch and symptoms dont improve, a healthcare professional may prescribe something stronger. Possible options include topical or oral medications.
Topical medications include econazole (Ecoza) or oxiconazole (Oxistat), while oral medications include itraconazole (Sporanox) or fluconazole (Diflucan).
Oral antifungal medications may cause unpleasant side effects, such as upset stomach and headaches. If you experience any of these side effects, be sure to discuss them with a doctor.
Common symptoms of jock itch in the affected area include:
- redness
- persistent itching
- burning sensation
- flaking, peeling, or cracking skin
- rash that gets worse with exercise or activity
- changes in skin color
- rash that doesnt improve, worsens, or spreads after using OTC hydrocortisone (anti-itch) cream
Jock itch typically affects the groin and inner thighs. It may spread to the abdomen and buttocks, but it usually doesnt develop on the scrotum.
A group of fungi called dermatophytes cause jock itch. These fungi naturally live on your skin and typically dont cause problems. However, when you remain in sweat-soaked clothes after exercising, prolonged exposure to moisture can allow the fungi to multiply quickly.
When you have an overgrowth of dermatophytes in your groin area, it causes the infection known as jock itch.
The fungus that causes jock itch is highly contagious. You may get the fungal infection through close personal contact with a person who has jock itch or through contact with that persons unwashed clothing.
Risk factors for jock itch
If the following factors apply to you, you might have a higher risk of jock itch:
- Youre male.
- Youre a teenager.
- You have overweight or live with obesity, which increases how many skin folds you have. The fungi that cause jock itch thrive in sweaty skin folds.
- You have a tendency to sweat, which increases the moisture of the skin and encourages dermatophytes to multiply.
- Your immune system doesnt function as it should due to an underlying health condition or treatment for a condition. People who are immunocompromised have
a higher risk of fungal infections like jock itch than those whose immune systems work at full capacity. - You wear a lot of tight clothes.
- You live with diabetes, which can
increase your risk for fungal skin infections.
Your doctor will likely be able to diagnose jock itch by performing a physical exam and inspecting the affected area of skin.
In some cases, your doctor may take some scrapings of skin cells from the area to help diagnose the condition. This may also help rule out other skin disorders, such as psoriasis.
There are several ways to reduce your risk for jock itch, including:
- Practice good hygiene. Regular hand washing can greatly reduce your risk of getting this infection from someone else. Its also important to keep your skin clean and dry, especially the area around your groin.
- Wash the area regularly with soap, and dry the area thoroughly after bathing. Applying baby powder around your groin can also be helpful for preventing excess moisture.
- Avoid tight-fitting clothing. Tight clothes can rub or chafe your skin, which can make you more susceptible to jock itch. You may want to try wearing boxer shorts instead of boxer briefs.
- Wear loose clothing in hot or humid weather. Loose clothing can prevent sweating and the warm, moist environment in which fungus thrives. Make sure you wash any workout clothes or athletic supporters after each use.
- If you have athletes foot, seek treatment quickly. The same fungi that cause jock itch can also cause athletes foot, and vice versa. You can avoid spreading it to your groin area by making sure you dont use the same towel on both your feet and your groin.
If your symptoms dont improve after 2 weeks of home treatments, you should make an appointment to see your doctor. You may have developed a secondary infection that needs prompt treatment.
If you dont already have a dermatologist, you can browse doctors in your area through the Healthline FindCare tool.
Jock itch is a contagious fungal skin infection that develops in skin folds like the armpits and buttocks.
The fungi that cause it, called dermatophytes, already live on your skin. But they can cause a skin infection if you wear sweat-soaked clothes for too long after physical exertion.
Its most common in males, teens, and folks who have overweight, as well as those with less active immune systems or diabetes.
The infection is usually mild, and you can treat it at home by applying OTC creams, regularly cleaning the area, and maintaining good hygiene.
If symptoms dont improve after 2 weeks of home remedies, consult a healthcare professional. A doctor may prescribe stronger medications for severe or stubborn jock itch.