Is dog fungus contagious to humans

Identifying and Treating Fungal Infections in Dogs
By Reyna Gobel
Bacteria and viruses are what typically spring to mind hen pet parents think infection, but fungi can also be to blame. While not as common as bacterial or viral infections, fungal infections can be just as serious. Dogs can contract fungal infections from other animals, from the environment, or as a result of the overgrowth of fungi that are naturally present on their own bodies. Every pet is potentially at risk for contracting a fungal infection, and an accurate diagnosis is necessary before appropriate treatment can begin. Read on to learn more about fungal infections in dogs.
Fungal Skin Infections
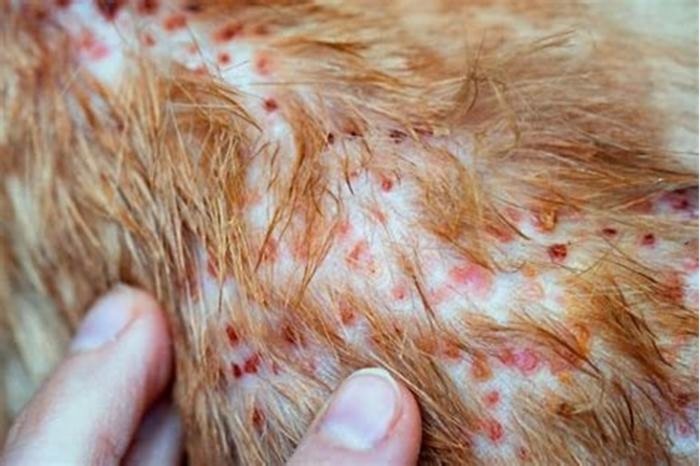
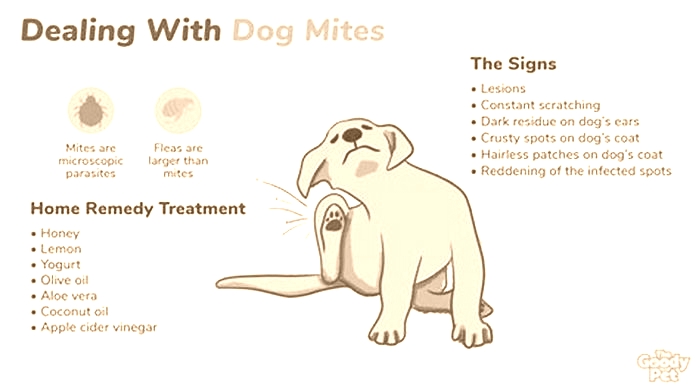
When your dog starts scratching himself more than is normal, it can be hard to tell whether its because of an allergy, flea bites, infection, or something else. Excessive itching can be quite worrisome, especially if your dog develops bald spots or damages his own skin as a result.
One telltale sign of fleas is the presence of flea dirt (small black clumps of flea feces) on your dogs skin and fur. If you see flea dirt or actual fleas, treat him right away. But if fleas or ticks arent to blame, dont self-diagnose or rely on Dr. Google, warns Dr. John DaJong, a veterinarian at Newton Animal Hospital in Massachusetts. After performing a complete physical exam, your veterinarian can conduct specific tests to help diagnose the problem and identify whether a fungal infection is to blame.
Lets look at two common types of fungal infections that affect the skin of dogs and how to treat them.
Ringworm
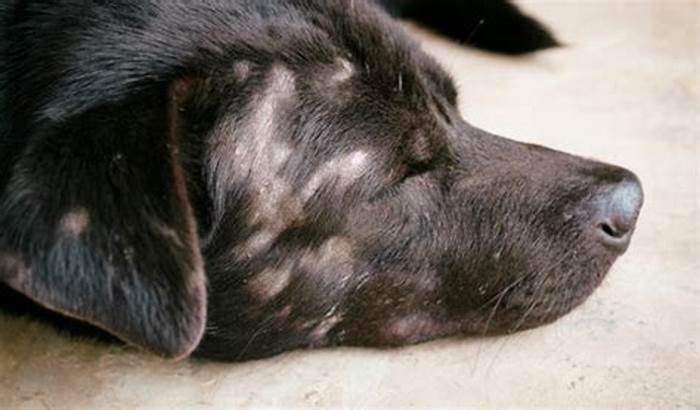
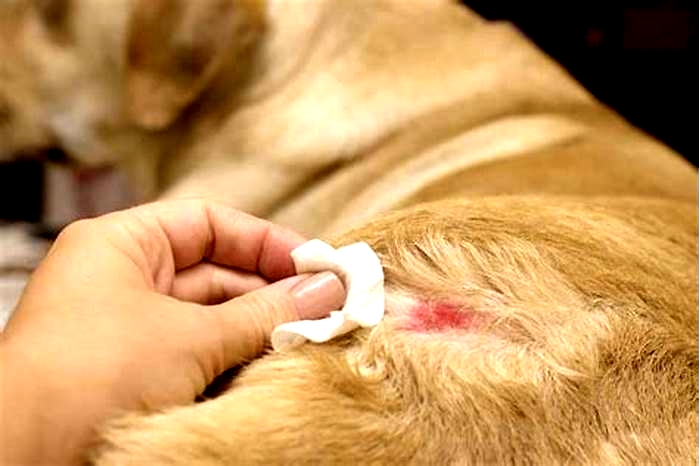
Ringworm is a common fungal infection in pets. It can affect a dogs skin, fur, and also the nails. Common symptoms include hair loss, itching, flaky or crusty skin, and misshapen or brittle nails. While you should treat any infection as soon as possible, time is of the essence with ringworm because it can easily spread to other household animals and humans, says Dr. Andrew Rosenberg, a veterinarian at Riverdale Veterinary Dermatology clinic in Riverdale, New Jersey.
To diagnose ringworm, your veterinarian will perform a fungal culture of hair or skin cells or a microscopic examination of a hair sample. Depending on the severity of the infection, ringworm may be treated with medicated baths and dips and/or oral antifungal medications. Vacuuming and disinfecting the house will also help lessen the chances that ringworm will spread between pets and people.
Yeast Infection
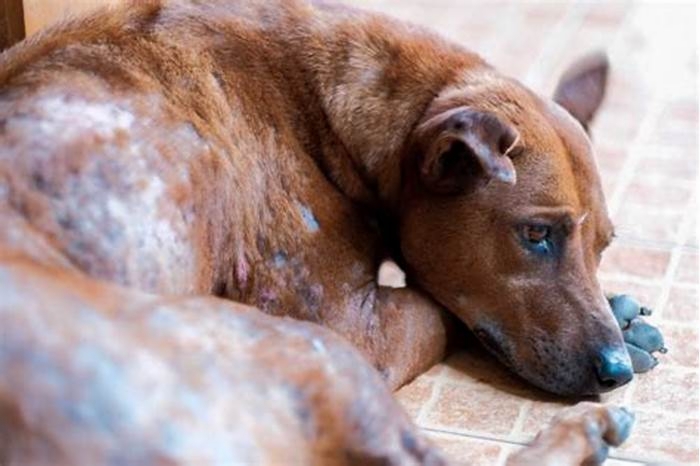
Overgrowth of yeast on a dogs body can lead to irritating yeast infections, commonly affecting the skin, paws, and ears. These infections can be extremely uncomfortable for dogs, says Rosenberg. Theyre generally secondary to allergies or other conditions that disrupt the skins ability to control the yeast that normally live there.
If I suspect a dog might have a yeast infection, I take an impression smear of the area that might be infected and look at it under a microscope, Rosenberg says. When the slide is stained, the yeast look like little purple peanuts.
Treatment normally involves an antiseptic or antifungal drug applied to the skin. Oral medications may be necessary in severe cases. Unlike ringworm, yeast infections arent contagious to other pets or people. To prevent yeast infections from recurring, its important to treat any underlying conditions as recommended by your veterinarian.
If your pet is constantly itching and scratching, schedule an appointment with your veterinarian. Unfortunately, not all conditions can be solved with one visit. Sometimes it could take several visits to pinpoint the cause of your dogs itching or require a visit to a veterinary dermatologist, Rosenberg says.
Systemic Fungal Infections
Fungal infections on the surface of the body are bad enough, but those that invade deeper structures can have even more serious consequences. Lets look at several common types of systemic fungal infections in dogs and how to treat them.
Blastomycosis
Blastomycosis is most commonly diagnosed in dogs that have spent time in Mississippi, Ohio, Missouri, Tennessee, the St. Lawrence River valley, the mid-Atlantic, and around the Great Lakes because the types of soil that are typically found in these areas support the growth of the fungus. Dogs that spend time sniffing around in the dirt are at risk for inhaling fungal spores, which can lead to a lung infection, says Dr. Jennifer Coates, veterinarian and author of Dictionary of Veterinary Terms, Vet-Speak Deciphered for the Non-Veterinarian. From there, the organism can travel almost anywhere in the body. According to Coates, common symptoms include poor appetite, weight loss, coughing, difficulty breathing, limping, eye problems, skin lesions (particularly around the toenails), enlarged lymph nodes, and fever. If the disease is caught early enough, treatment with an oral anti-fungal medication can be curative.
Cryptococcosis
While cats are more commonly infected with the fungus Cryptococcus, Coates says dogs tend to develop a more severe form of the disease. The fungus is present in soils world-wide but may be especially prevalent in areas where pigeons and other birds congregate. As is the case with blastomycosis, dogs typically inhale the Cryptococcus fungus, leading to a lung infection. It can then spread almost anywhere in the body, which can cause symptoms ranging from lethargy, coughing, nasal discharge, eye problems, skin lesions, and even seizures and other neurologic abnormalities. Coates warns that treating cryptococosis can be difficult. Oral antifungal medications may need to be given for a year or more and some dogs will still succumb to the disease.
Coccidioidomycosis
Dogs can get coccidioidomycosis (also known as Valley Fever) from inhaling dust or dirt that contains coccidioides fungal spores,says Dr. Carol Hillhouse, a veterinarian in Panhandle, Texas. It tends to grow in desert areas with little rain and sandy soil, such as California, Nevada, Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas, she says. Strong winds, earthquakes, construction areas, and even crop harvesting can stir up the spores into the air.
Once the spores are inhaled, the fungus may simply cause a chronic cough, Hillhouse says. In other cases, especially if immunosuppressed, the dog may develop pneumonia or the fungus can spread to other areas in the body, such as bone or the eyes, she says. It can be difficult to diagnose, and usually requires radiographs, blood, and cell testing. Valley fever requires long-term treatment with oral antifungal medications, but the prognosis is pretty good if caught early, she says.
Histoplasmosis
Another soil-borne fungus, Histoplasma, prefers the temperate climates of Ohio, Mississippi, and Missouri River Valleys, Hillhouse says. This fungus grows best in nitrogen-rich soil, such as bird and bat excrement, and is usually acquired by inhalation of the organism from the environment.Infected dogs can show weight loss, fever, cough, eye inflammation, vomiting, and diarrhea, she says. Often, a combination of blood and urine tests, as well as radiographs, are used to make the diagnosis. Sometimes biopsies are required as well. Treatment involves long-term fungal medication, but prevention is best by restricting access to soil that is contaminated with bird or bat droppings.
Aspergillosis
Infections with Aspergillusfungus are usually limited to a dogs nasal passages. Aspergillosis can affect dogs residing in almost any part of the country since the fungus is present in most soils. Treatment typically involves anesthetizing the pet and infusing his nasal passages with a liquid anti-fungal medication. Most dogs will recover if treated appropriately, although a second treatment may be necessary in some cases.
Preventing Fungal Infections in Dogs
Fungal infections in dogs range from localized annoyances to potentially fatal systemic diseases. Prevention is not always possible, but common sense measures can help. If you live in an area where a certain type of fungal infection is endemic, avoid high risk environments. Pets with ringworm should be isolated to limit the spread of the disease to people or other animals. Finally, appropriately manage any underlying health problems that increase your dogs risk for developing a fungal infection.
5 Skin Conditions Dogs Can Pass On To Humans
If you are like most dog parents, then you frequently give your dog hugs and snuggle up to them.
You might even allow your dog to sleep in the same bed as you.
Did you know there are some pretty serious skin problems that you can get from your dog?

Here are 5 dog skin conditions (plus one painful disease) that dogs can pass onto humans
How Dog Skin Conditions Transfer To Humans
Dogs typically get these skin conditions while playing outside, in dog parks, or while roaming the neighborhood.
However, believe it or not, your dog can actually pass on a skin condition to you without having the skin condition himself!
For example, one way that a dog can pass on a skin condition is by being petted. If someone pets your dog and they have a skin condition, if your dog rubs on you or you pet him, then you have a good chance of getting the skin condition yourself.
Who knew???
Like people, all animals carry germs But pets also carry certain bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi that can cause illness if transmitted to humans. Humans get these animal-borne diseases when theyre bitten or scratched or have contact with an animals waste, saliva, or dander. Source
5 Skin Conditions Dogs Can Pass Onto Humans
#1 Im sure youve heard of people getting Staph Infections, like MRSA, while in the hospital. Did you know that you can get a Staph Infection from your dog? Some Staph Infections cannot be treated with common antibiotics. Dogs pick up the bacteria for a Staph Infection from a person. Then, if your dog bites another person (or, if his saliva simply enters through a cut on the persons hand or some other open wound), the Staph Infection gets passed on to that person as well.
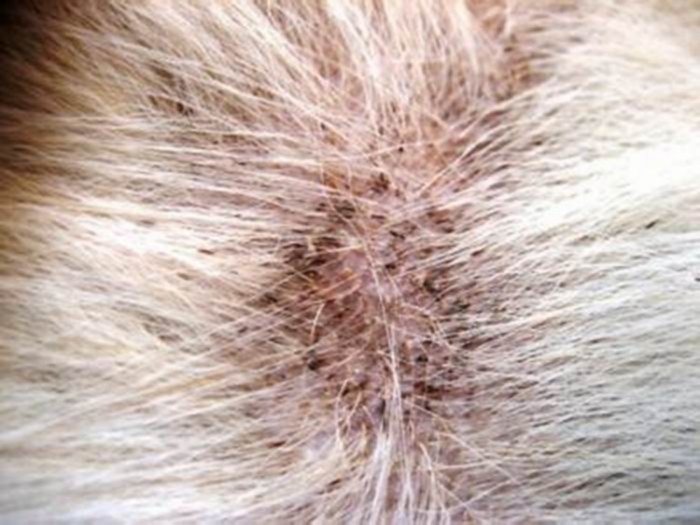
#2 Another skin condition that you can get from your dog is Scabies. Scabies is caused by a mite that is known to hang around kennels and pet shops. Scabies is a red bumpy rash with white flakes and the mites (known as Sarcoptic Mites and Mange) appear to be moving under the skin. Ive had experience with Scabies. When Iwas around 8, my entire family got infected with Scabies. It itches really bad. Our family doctor treated it with a prescribed lotion. A friend of mine also got Scabies from a dog that she rescued.
Here are 3 other dog skin conditions that can be passed on to humans:
#3 Ringworm This is actually a fungus, not an actual worm. (Its highly contagious to humans and other pets.)
#4 Hookworm This can cause abdominal pain, anemia, and diarrhea. (Heres more about how hookworms can infect humans.)
#5 Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever Your dog gets this from a tick bite. (My same friends dog also got Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever, in addition to the Scabies.)
What About Lyme Disease?
While not a skin problem, another serious medical condition that you can get from your dog is Lyme Disease.
Ifa tick that has infected your dog getsonto your own body, then you would be exposed to Lyme Disease as well. Lyme Disease can be painful and debilitating for both humans and dogs.
Heres how to tell if your dog has Lyme Disease from a tick bite.
photo by Mike Baird
I have 2 Miniature Pinschers. My husband and I consider them our 4-legged kids.
Fungal Infections in Dogs
Oomycosis (also called pythiosis) is a disease caused by Pythium insidiosum, which is not a true fungus but a water mold related to algae. It occurs in some tropical and subtropical areas of the world and is seen in warmer to temperate sections of the US. In dogs, pythiosis is most often encountered in Southeast Asia, eastern coastal Australia, South America, and the United States, especially along the Gulf coast. In the US, the disease most often is seen in fall and winter months.
These organisms cause disease when animals come into contact with the infecting zoospores in water, usually by ingestion. Pythiosis most often affects the gastrointestinal tract in young adult dogs, especially Labrador Retrievers. The usual site of infection is the stomach and the adjacent intestinal tissues, but any part of the gastrointestinal tract may be infected. Affected dogs often will have a history of upper gastrointestinal tract obstruction and may have an abdominal mass the veterinarian can feel during examination. Common signs include vomiting, weight loss, and loss of appetite. The weight loss can be severe, but affected dogs usually do not appear generally ill until the infection is well advanced.
Less frequently, dogs will have a pythiosis infection concentrated in the skin and adjacent tissues. A wound has usually allowed the entry of the infective zoospores into the skin tissues. Many of these animals have a history of swimming or being in swampy areas. Non-healing, tumor-like nodules may be present. They often grow rapidly. Some lesions may have a focused area of dead cells and a spongy appearance. Such lesions are usually on the legs, neck, near the place where the tail connects to the body, or on the perineum (the space between the anus and scrotum (male) or vulva (female)). They can, however, be seen anywhere on the body.
Lagenidiosis is a disease involving theskin, the area beneath the skin, and multiple parts of the body, most often the legs, mammary glands, perineum, or trunk. It has been recently reported in dogs from the southern United States. Lagenidiosis also is caused by a water mold (Lagenidium species). There are at least two species of Lagenidium that affect dogs, one of which progresses quickly. The slower developing form of lagenidiosis is very similar to the skin form of pythiosis. The faster developing form can involve multiple, organs across the body. Internal lymph nodes, the lungs, and large blood vessels (such as the aorta or vena cava) may be affected. This can lead to large bulges in the wall of the blood vessels (called aneurysms) that can rupture and cause sudden death.
Dogs exposed to warm, standing fresh water are more likely to be in contact with the infectious zoospores and may have increased risk for both pythiosis and lagenidiosis. Reports of animals being infected with no known history of being near water suggests that animals may be infected by contact with resistant spores that form in wet soil and on grass.
The diagnosis of lagenidiosis and pythiosis is made with laboratory tests including cultures and blood tests. The treatment of choice for pythiosis and lagenidiosis has been aggressive surgery to remove infected tissue, but the disease is often too extensive at the time of diagnosis to allow complete removal. Whenever possible, complete amputation of affected limbs may be curative. Your veterinarian may recommend surgery followed by treatment with antifungal drugs. Approximately 20% of dogs will respond to longterm antifungal treatment. For most infections the outlook is guarded to poor, even though there have been advances in treatment. In some dogs, a therapeutic vaccine (one given to treat a disease rather than prevent it) has helped cure the condition.
Also see professional information regarding oomycosis