What are the signs of mites
What Dust Mite Bites Look Like and How to Get Rid of Them
Dust mites dont truly bite, but they can cause rashes and other allergy symptoms. Regularly washing your bedding and vacuuming floors may help get rid of dust mites, while antihistamines, decongestants, or allergy shots may help ease itching and discomfort.
Dust mites are one of the most common allergy and asthma triggers that lurk inside your own home.
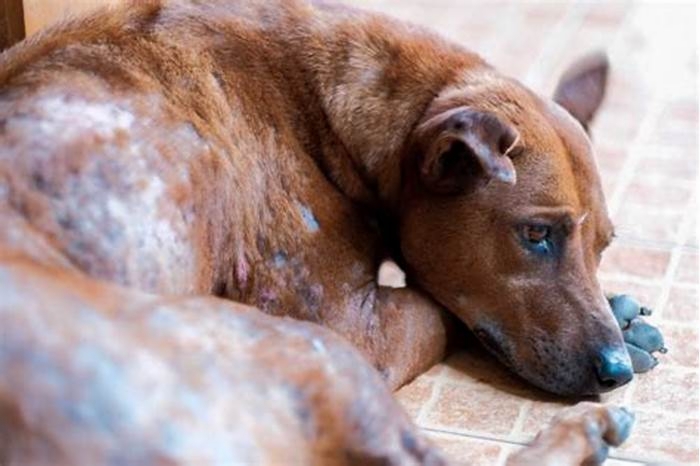
While these microscopic creatures resemble small bugs, dust mites dont actually leave bites on your skin. They can, however, cause skin rashes. Youre also more likely to have other allergy symptoms, such as sneezing and postnasal drip.
Dust mites arent to be confused with bedbugs, which are a separate type of species that leave visible bites on your skin.
If you have continuous allergy symptoms throughout the year, it may be worth talking to a doctor about possible dust mite allergies. While difficult to get rid of completely, there are ways you can manage dust mite populations in your home while also treating your allergies.
Dust mites can be difficult to detect due to their small size. These microscopic arthropods are estimated to be only 1/4 to 1/3 millimeters long. You can only see them under a microscope, and even then, they only look like small white spider-like creatures.
Males dust mites can live over a month, while female dust mites can live up to 90 days.
The reason why dust mites are so prevalent in peoples homes is that they feed off of dead skin cells. On an average day, one person may shed 1.5 grams of dead skin cells, which can feed up to one million dust mites at a time.
Dust mites make their homes in places where dead skin cells are most likely to accumulate, such as bedding, furniture, and carpeting. Rugs and stuffed animals also make good homes for dust mites.
While you can find dust mites all over the world, these creatures tend to favor hot and humid climates. Since they can burrow themselves deep into cloth fibers, they can also travel with you when you move or are on a vacation or business trip.
Dust mites themselves are allergenic, meaning they can cause allergies. They also leave behind skin and fecal matter that may also trigger allergies.
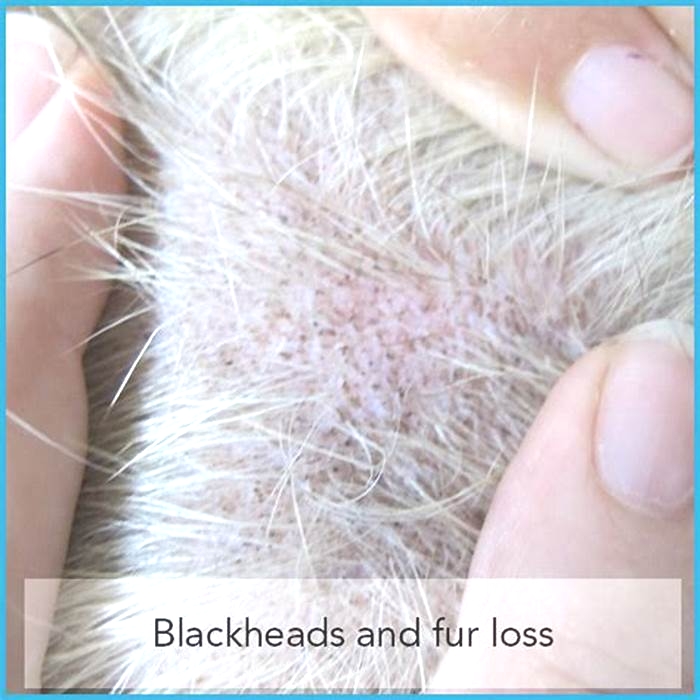
While other bugs you encounter may bite, dust mites themselves dont actually bite your skin. However, an allergic reaction to these pesky creatures may induce skin rashes. These are often red and itchy in nature.
Allergic reactions to dust mites are common and typically caused by inhaling the mites skin and fecal matter materials.
If you have a dust mite allergy, you may experience symptoms year-round. You may also notice that your symptoms peak during the hot, humid summer months. Common signs of a dust mite allergy include:
- sneezing
- coughing
- postnasal drip
- runny or stuffy nose
- itchy, water eyes
- red, itchy skin
- itchy throat
Depending on the severity of your dust mite allergies, this condition may also trigger asthma.
You may notice wheezing, coughing, and chest pain as a result. Your symptoms may be worse at night when youre lying down. The more you stay indoors, the more you may be prone to dust mite complications.
The best way to treat allergies is to get rid of the underlying culprit. Depending on the severity of your symptoms though, you may need immediate relief.
Talk to your doctor about the following treatment options for dust mite allergies:
- Over-the-counter (OTC) antihistamines. These work by blocking histamine, which is released when your immune system encounters an allergen. Common antihistamines brands include Zyrtec, Claritin, Allegra, and Benadryl.
- Decongestants. If your allergies continuously cause stuffy nose, postnasal drip, and sinus headaches, you may benefit from an OTC or prescription decongestant to break up the mucus.
- Prescription allergy medications. Possibilities include oral leukotriene receptor antagonists and nasal corticosteroids.
- Allergy shots. These work by injecting small amounts of a specific allergen into your system so you build up immunity over time. Allergy shots are administered weekly over the course of several months or even years and are best for severe allergies that arent alleviated with medications. You must undergo allergy testing before getting allergy shots.
Dust mites are difficult to get rid of completely, but removing as many as possible from your home can help prevent allergic reactions.
The best way to get rid of dust mites is to target the areas they tend to live in and thrive. These include:
- bedding
- pillows
- carpets
- rugs
- pet bedding and furniture
- furniture
- blinds and curtains
- toys and stuffed animals
Frequent vacuuming, wet mopping, dusting, and washing can all treat dust mites. You dont need any specialized products. You just need to make sure you wash bedding in hot water and use wet cloths that can properly trap dust when you clean.
Prevention is key to avoiding allergies, including dust mites. It may be challenging to prevent them altogether, but you can take the following steps to control the dust mite population in your household:
- Avoid carpeting in your home as much as possible.
- Vacuum and deep clean all carpet and rugs as often as you can.
- Dust regularly, paying extra attention to blinds, furniture crevices, and other small areas where dust mites may accumulate.
- Keep the humidity in your home under 50 percent to ward off the conditions dust mites thrive in.
- Use certified allergen-capturing filters in all air conditioning units and vacuums to make sure dust mites and their fecal matter are fully captured.
- Wash all bedding weekly using hot water.
- Use zippered mattress and pillow covers to prevent dust mites from entering your bedding.
Its important to note that pesticides do not get rid of dust mites.
Although dust mites dont bite humans, their widespread presence in your home can lead to uncomfortable allergy symptoms, including skin rashes.
Dust mites are prevalent in most homes, so regular cleaning and other preventive measures are key to stopping their large numbers while also alleviating your allergies.
If you continue to have allergies despite dust mite prevention, see an allergist for help.
What do mite bites look like?
Mites are small arachnids that may might humans. People may not realize they have come in contact with mites until they develop itchy, red, or discolored bumps that resemble bites.
The term mites refers to microscopic arthropods that feed on plants, insects, animals, and even humans. Mites range from
Continue reading to learn how to identify and treat mite bites. We also discuss possible alternative bites.
Some mites do bite animals and humans. Examples of mites that bite humans include:
Chiggers
Chiggers are the larva of the
While adult chiggers feed on decaying material in soil, their larvae feed on the skin cells of living hosts. When a chigger attaches to a persons skin, it secretes digestive enzymes that soften the epidermis, causing skin rashes.
Symptoms
Chigger bites create clusters of small red bumps on the skin accompanied by intense itching that can last for
Treatment
A person can treat chigger bites using:
- oral antihistamines
- topical corticosteroid cream
- cold compresses
Demodex mites
Demodex mites feed on dead skin cells and oil inside hair follicles. There are
D. folliculorum mites
- the cheeks
- the nose
- the chin
- the temples
- the eyelashes
- the eyebrows
- the ears
- the skin folds that extend from the nose to the corners of the mouth
Symptoms
While a few D. folliculorum mites can live on humans completely unnoticed, an infestation can lead to undesirable symptoms, including:
- patches of red, inflamed, or dry skin on the face
- inflamed, crusty, or watery eyelids
- itchy skin
- acne-like blemishes
Treatment
A person can use topical insecticides, such as crotamiton or permethrin cream to treat Demodex bites.
To prevent the bites from worsening, a person should:
- clean the face twice daily
- avoid oil-based cleansers
- exfoliate
Oak mites
Oak mites typically feed on midge fly larvae, but they can bite people if they remain on the skin.
The oak leaf gall mite has caused a series of human outbreaks in Missouri, Nebraska, and Texas over the years, and causes yearly outbreaks in Kansas.
Symptoms
Oak mite bites look similar to chigger bites.
People may develop itchy red welts on their face, neck, arms, or upper body.
Treatment
A person can treat oak mite bites by using:
- calamine lotion
- oral antihistamines
- over-the-counter (OTC) hydrocortisone product
Scabies
Scabies is a skin condition caused by an infestation of
The S. scabiei mite burrows into the upper layer of the skin, where it reproduces and lays eggs.
Scabies is contagious. According to the
Symptoms
A scabies infestation can lead to an itchy, red skin rash accompanied by intense itching. The rash may contain tiny bumps, hives, or welts under the skin.
Scratching the affected skin can lead to open sores and increase a persons risk of infection.
Treatment
Doctors can treat scabies with oral medications and topical ointments that kill S. scabiei mites and their larvae.
Doctors may also prescribe antihistamines to reduce itching and antibiotics for infections.
Mites are so small that people are unable to see or feel the bites until after a mite has bitten them.
Unlike other insect bites or stings that form a single lump on the skin with a noticeable puncture site, mite bites induce skin rashes on the legs, arms, and trunk.
General signs to look for include:
- small, hard bumps on the skin
- red patches of skin
- irritation, itching, or swelling near the bites
According to the
They feed on dead skin and dander that falls off of humans and pets. Dust mites live in house dust, mattresses, furniture, and carpets. These tiny creatures do not bite or live on humans.
Instead, proteins in the exoskeletons and feces of dust mites can induce allergic reactions in people.
Exposure to mites can lead to patches of small, red bumps on the skin accompanied by the following respiratory symptoms:
- nasal congestion and sneezing
- itchy, red, or watery eyes
- itchy nose, mouth, or throat
- a cough
- chest tightness
- difficulty breathing
- wheezing
The Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America (AAFA) warn that dust mites can worsen a persons asthma.
Treatment
Treatment for dust mite allergies include:
- over-the-counter (OTC) antihistamines
- oral or liquid decongestants
- nasal sprays containing corticosteroids or cromolyn sodium
Immunotherapy is an effective treatment for dust mite allergy, according to the AAFA. Immunotherapy involves exposing a person to progressively larger doses of an allergen.
People cannot eliminate dust mites from their homes entirely, but the following tips can help reduce the effects of dust mites:
- frequently vacuuming, mopping, and dusting
- washing sheets, pillowcases, clothing, and any other household fabrics in hot water (
130-140F ) - wiping dust with a damp cloth
- using a dehumidifier or air conditioner to reduce humidity levels in the house
- removing carpets and curtains
- covering mattress, pillows, and cushions with hypoallergenic or dust-proof covers
The following precautions can help prevent mite bites outdoors:
- applying insect repellants, such as DEET or Picaridin
- wearing long boots, long trousers, and long-sleeve shirts when walking through tall grass or dense vegetation
- taking a hot shower or bath and washing clothes in hot water immediately after leaving an infested area
People should see a doctor if they believe they have scabies bites because S. scabiei mites can easily transfer from one person to another.
Bites from chiggers and oak mites rarely require medical attention. People can treat their symptoms with OTC antihistamines and decongestants.
Try not to scratch mite bites, as this can lead to an infection. Anti-itch cream and topical corticosteroids may help reduce itching and swelling.
People should contact a doctor if they experience signs of an infection, including:
- a fever
- chills
- the skin near the bite appears red, swollen, and warm
- fluid or pus leaking from the bite
House or dust mites that live in dust do not bite, but they can induce allergic reactions.
Chiggers are mite larvae that feed on skin cells and leave clusters of small, red bites on the legs and feet.
Most mites do not bite humans, but they may bite if they remain on a persons skin.
In general, mite bites cause mild skin irritation and itching and do not require medical attention. People can treat mite bites with OTC and prescription antihistamines, topical corticosteroids, and allergy injections.
People who believe they have scabies should seek immediate medical attention. The mites responsible for this skin condition can live under the skin for several months.
Scabies infestations are highly contagious, so people must seek treatment as soon as possible to prevent further transmission.