What can I put on my dogs skin fungus

Coconut Oil for Dogs: Is it Really Good for Them?
Coconut oil has become a popular supplement for people. In humans, some evidence suggests that consuming coconut oil in limited amounts may offer possible benefits, including boosting the immune system, aiding in weight loss, acting as an anti-inflammatory and antifungal agent, and improving cognitive skills in patients with Alzheimers disease. Today, many experts debate how helpful eating coconut oil may actually be for people.
But pet owners are asking can coconut oil be beneficial to dogs? The answer is maybe. But that doesnt mean you should immediately feed your pet coconut oil or apply it to their skin. Heres what you need to know about coconut oil and dogs.
Science Behind Coconut Oil
Coconut oil comes from the meat of coconuts harvested from the coconut palm tree. Coconut oil consists of at least 90% saturated fats, most of which are medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs). Besides coconut oil, MCTs are often found in palmer kernel oil, butter, yogurt, milk, and cheese.
What are MCTs? MCTs are fatty acids that can be considered good fat. When consumed in moderation, MCTS can provide several benefits, including reducing skin inflammation. MCTs also metabolize quickly and provide an immediate source of energy. MCTs in coconut oil may help battle fungi and infection, support brain health, and lower cholesterol.
Can Dogs Have Coconut Oil? Pros and Cons
Can dogs eat coconut oil? Its possible consuming some coconut oil may offer internal benefits for dogs. The main MCT in coconut oil is lauric acid. Lauric acid has antimicrobial, antifungal, and antiviral properties. Coconut oil also has amounts of capric and caprylic acids, which are known for their antifungal effects. The oil also has both polyunsaturated and monounsaturated (fatty acids that support brain health and help lower cholesterol). Some research indicates that coconut oil may be helpful in aiding canine digestion, improving brain activity and mental function, and assisting with weight loss.
But is coconut oil good for dogs? These benefits dont mean you should go out and feed your dog coconut oil without veterinary approval. There hasnt been extensive research proving that coconut oil will definitively aid in many aspects of canine health. Vets may also debate how widely applicable (or relevant) these studies results are. Furthermore, feeding your dog coconut may work against some of the same conditions coconut oil is said to cure. For example, instead of helping with digestion, the fats in coconut oil can cause upset stomachs or diarrhea in dogs.
Additionally, coconut oil doesnt meet your dogs daily fat requirements. The acids in MCTs dont have enough omega-6 and omega-3 acids, and what it does contain isnt processed very efficiently. As for claims that MCTs protect against bacteria, viruses, and fungi, while the lauric acid in MCTs does kill germs in lab tests, there is no clear evidence that it can be used in sufficient quantities to offer dogs much protection.
When Applied Topically
You may be asking, Can I put coconut oil on my dog? In fact, applying coconut oil to your dogs skin may be helpful. Coconut oil can help soothe irritated areas like hot spots or restore moisture to itchy, dry skin. If your pet has dry, cracked paws, try a DIY paw balm with coconut oil as one of the ingredients.
To add some shine to your dogs coat, try using shampoos formulated for dogs that include coconut oil as an ingredient. A moisturizing dog shampoo containing coconut oil is ideal for hydrating dry fur, while a dog conditioner with coconut oil will help soften the hair.
Can I Use Coconut Oil as a Topical Antifungal Treatment?
If you think your dog may have a fungal issue, talk to your vet immediately and follow their recommended course of treatment. While coconut oil does have antibacterial and antifungal properties, it is unclear how well this translates to canine skin disease, Dr. Linda Simon says. The vets treatment will depend on the species of fungus causing infection, how serious or widespread the infection is, and the age and health of the dog, notes Dr. Jamie Whittenburg. She explains that most mild to moderate fungal infections can be treated topically with a combination of shampoos and creams.
If your dog has a musty smell or greasy skin (resulting from an overgrowth of yeast), your vet may recommend using a medicated wash. For severe or widespread fungal infections, especially in dogs with immune system dysfunction, your vet may prescribe oral medications. These medications can cause liver issues, so serial blood work should be performed to monitor the pets health, Dr. Whittenburg adds.
Your vet may recommend coconut oil as part of a skin supplement regime to strengthen the skin barrier and reduce itchiness or dry skin, according to Dr. Simon. Dr. Whittenburg adds, In most cases, theres no harm in utilizing topical coconut oil on a dog. However, it is messy, can clog pores, and may cause the dog to lick the affected area more, leading to increased pain, inflammation, and infection.
How Can I Safely Give Coconut Oil to My Dog?
Before applying coconut oil topically or giving your dog some to eat, discuss these options with your vet. If they approve of you giving coconut oil to your pet, choose unrefined coconut oil, also called virgin coconut oil. Better yet, look for cold-pressed oil, which uses a method to preserve nutrients.
If youre feeding it to your dog, be aware that oils have different smells and tastes. Some have a bold coconut taste, while others are bland. Some are buttery and smooth, while others are nutty. You may have to experiment a bit to find one your dog likes. Alternatively, your vet may recommend trying coconut oil skin and coat supplements designed specifically for dogs.
If you do put a small amount of coconut oil on your dog and they lick it off, that likely wont cause much harm. But feeding it to them can definitely lead to both weight gain and gastrointestinal disturbances, Dr. Whittenburg says. Dr. Simon agrees, explaining that long-term feeding of coconut oil can lead to obesity in dogs and even trigger pancreatitis (a potentially life-threatening condition caused by inflammation of the pancreas). In the short term, your dog may experience greasy stool or diarrhea.
To use coconut oil topically, apply it to the skin about once a week, and let it be absorbed for a few minutes. After five minutes or so, rinse your dog off. If they still feel greasy or oily to the touch, you can follow up with a light shampoo and rinse.
Because of the potential risks associated with the topical or internal use of coconut oil, Dr. Whittenburg doesnt recommend that dog owners select products specifically for their coconut oil content. In the case of hardened noses or paw pads, for example, using soothing products made with coconut oil can help soften.
Yeast Infections in Dogs
What Are Yeast Infections in Dogs?
Does your dog frantically itch their skin? Have you noticed a bad smell or greasy fur when you pet them?
If so, they may have a yeast infection.
Yeast are fungal organisms that normally live on a dogs skin without causing problems. However, when a dogs immune system weakens or an underlying health condition, such as hypothyroidism, is present, yeast can overgrow and cause an infection.
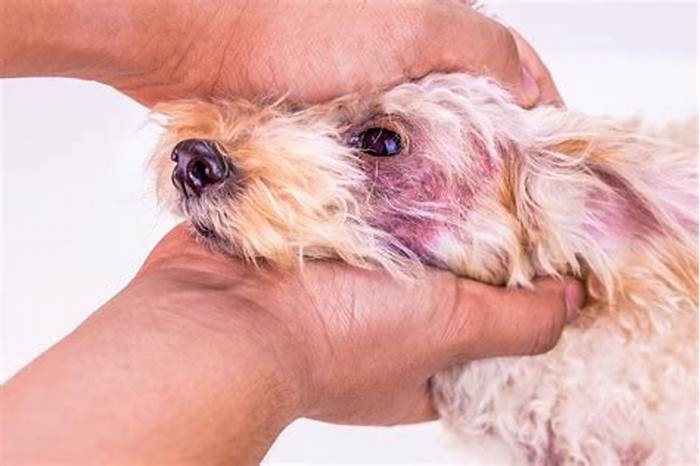
The yeast that commonly causes skin infections in dogs is Malassezia, which grows on warm, moist areas of the skin. Yeast infections cause extreme itchiness and changes to the skin, such as thickening and discoloration over time.
Yeast infections in dogs are common among pups of all ages.
While yeast infections in dogs are not considered medical emergencies, they should be treated by a veterinarian immediately to prevent symptoms from worsening. If left untreated, yeast infections can cause extreme discomfort, which can lead to a decreased appetite and lethargy, necessitating prompt veterinary care.
Because yeast infections typically develop secondary to an underlying illness or suppressed immune system, they are not contagious among dogs or to pet parents.
Types of Yeast Infections in Dogs
Yeast infections can affect various areas of the skin, including the ears, skin folds, paws, armpits, vulva, and groin.
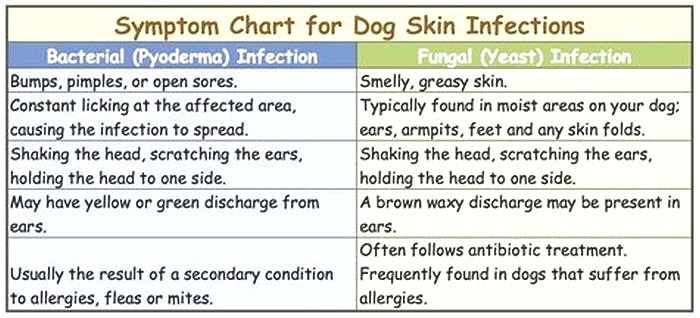
EarsYeast infections of the earalso referred to as yeast otitiscause a thick, brown discharge and strong odor in the ear canal. Affected dogs repeatedly scratch their ears to try to relieve the discomfort. They may also shake their heads and develop a head tilt. Ear infections are commonly related to food allergies.
SkinYeast dermatitis refers to a yeast infection anywhere on the skin. Affected dogs have a musty odor, greasy coat, flaky or thickened skin, and hair loss. They tend to lick the affected areas of the body, which leads to brown discoloration of the skin over time.
Dermatitis, which is often due to allergies or a suppressed immune system, can affecta dogs skin folds, armpits, vulva, and groin.
PawsYeast infections that affect the paws are generally related to environmental allergies, such as allergies to grass or pollen. Dogs constantly chew or lick their itchy paws, which leads to brown discoloration between the paw pads. Over time, open sores can develop on the paws.
Symptoms of Yeast Infections in Dogs
Signs of yeast infections in dogs can vary depending on what area of the body is affected.
Symptoms of yeast otitis may include:
Symptoms of yeast dermatitis may include:
Itchy skin
Small, red bumps on the skin
Brown discoloration of the skin
Frequent licking or chewing of the affected area
Greasy hair coat
Thickened skin
Strong odor
Symptoms of a yeast infection affecting the paws may include:
Licking and chewing the paws
Brown discoloration of the skin and fur
Red, moist areas between the paw pads
Causes of Yeast Infections in Dogs
Yeast is opportunistic, which means that although it is naturally present on the skin, it can cause an infection when conditions are favorable.
Yeast infections in dogs can develop if a pup has a weak immune system or an underlying health condition. Underlying environmental or food allergies can predispose dogs to developing yeast infections.
Skin parasites, including fleas and mites, can cause dogs to repeatedly itch their skin, which disrupts the normal skin barrier, making an infection more likely.
Some breedssuch as Pit Bulls, Boxers, and Cocker Spanielsare more frequently affected by yeast infections.
How Veterinarians Diagnose Yeast Infections in Dogs
A vet may use several tests to diagnose a yeast infections in dogs.
First, they will gather a through medical history, including when the symptoms started, if your pet is taking any medications, and if they have previously been diagnosed with any health conditions.
Next, your veterinarian will perform a full physical exam to check your dogs overall health. They may also perform blood work to check for any abnormalities.
Additional tests will depend on what your veterinarian finds during the initial exam, but may include the following:
Tape impressionDuring this test, your vet presses a piece of clear tape to the affected area of skin to collect a sample. Its then stained and examined under a microscope to identify yeast.
CytologyA cotton swab is used to collect a sample from the affected area, and it is then rubbed gently onto a microscope slide. The sample is then stained and examined under a microscope to look for yeast.
CultureA sterile cotton swab is used to collect a sample from the affected area. It is then sent to a lab to identify the type of organism present.
Skin biopsyFor chronic infections or those that are unresponsive to treatment, a small sample of skin can be taken and sent to a lab for a more accurate diagnosis.
Treatment of Yeast Infections in Dogs
Treatment for yeast infections in dogs will depend on the location and severity of the infection. Yeast dermatitis is often treated with antifungal medications and prescription shampoos.
If the infection affects only one area, a topical medication may be all that is needed. For more widespread infections, oral medications and frequent bathing can help resolve the issue.
Yeast otitis is typically treated with topical antifungal medications and steroids to reduce inflammation. Your veterinarian may recommend that you use a medicated ear wash prior to instilling ear medications.
Paw yeast infections may benefit from medicated antifungal wipes and oral medications, including antifungals and steroids.
Recovery and Management of Yeast Infections in Dogs
Because yeast infections in dogs often develop secondary to another health condition, they will not resolve without veterinary treatment.
Determining the underlying cause of the yeast infection and treating it accordingly improves treatment success. For example, if your dog has an underlying food allergy, an accurate diagnosis and treatment can help their skin improve.
It can take a few weeks to a few months for a yeast infection to fully resolve, depending on the severity. Most dogs start to feel relief from their symptoms in a week or two, but it can take several additional weeks for a pet parent to notice significant improvement to their skin and coat.
Prevention of Yeast Infections in Dogs
Ensuring your dog receives regular preventive care and vaccinations keeps them healthy and less likely to develop infections.
Additionally, health conditions that can lead to yeast infections in dogs can be caught and managed early during routine wellness visits.
Yeast Infections in Dogs FAQs
What food causes yeast infections in dogs?
Most of the food ingredients that cause allergies in dogs are proteins. Chicken is the most common food allergen related to yeast infections.
What happens if dog yeast infections go untreated?
If a dogs yeast infection is left untreated, it will progressively worsen and lead to extreme discomfort. Over time, the discomfort can cause the dog to become very sick.
What should I feed my dog when they have a yeast infection?
Unless the yeast infection is due to an underlying food allergy, its generally fine to continue your dogs usual diet. However, it is best to follow your veterinarians recommendations when deciding what to feed your dog.
Featured Image:SerhiiBobyk/iStock / Getty Images Plus via Getty Images
WRITTEN BY
Brittany Kleszynski, DVMVeterinarian
Dr. Brittany Kleszynski is a veterinarian and freelance medical writer who specializes in creating meaningful content that engages readers...