What does a cancerous rash look like
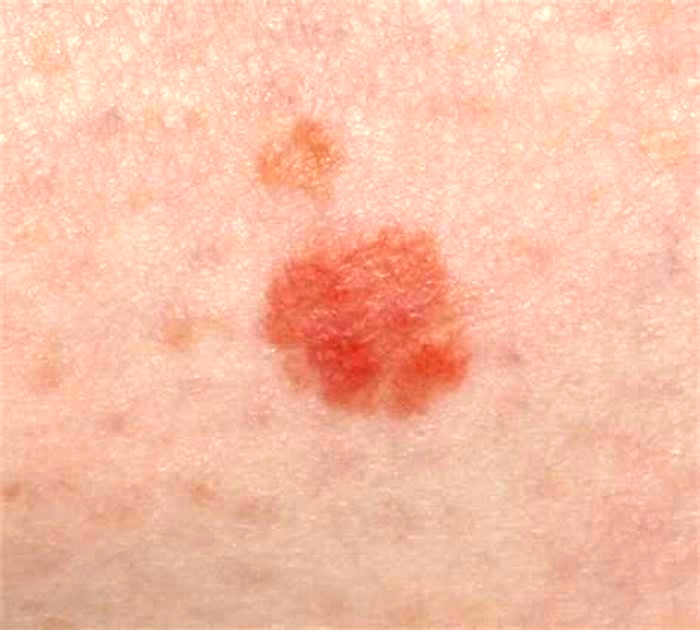
Skin Cancer Image Gallery
Skin cancer is by far the most common type of cancer. Nearly all skin cancers can be treated effectively if they are found early, so knowing what to look for is important.
There are many types of skin cancer, each of which can look different on the skin. This picture gallery contains some examples of the more common types of skin cancer, as well as some other non-cancerous types of skin growths. But skin cancers can look different from these examples. This is why its important to see a doctor if you have any lumps, bumps, spots, sores, or other marks on your skin that are new or changing, or that worry you for any other reason.
Is This Spot or Rash Skin Cancer?
Rashes on the skin, such as bumps or redness, typically result from contact with an irritant. But sometimes, they can be a sign of cancer. If a mole itches, bleeds, or changes shape, it may be a sign that you should get it checked out by a doctor.
Skin rashes are a common condition. They usually stem from something harmless, like a reaction to heat, medication, a plant like poison ivy, or a new detergent youve touched.
Rashes can show up on any part of your body, from your head to your feet. They can even hide in the cracks and crevices of your skin. Sometimes they itch, crust, or bleed.
Occasionally, bumps or redness on your skin can be a sign of cancer.
For example, if you notice an itchy mole on your chest that seems to be changing shape, theres a chance youre dealing with skin cancer.
Because cancer can be very serious even life threatening its important to know the difference between a rash caused by irritation and one caused by skin cancer.
This is why its important to talk with a dermatologist about any rash or growth thats new, changing, or not going away.
While skin cancers are often asymptomatic, meaning they dont show symptoms, they can be itchy.
For instance, basal cell skin cancer
Talk with your doctor about any itchy, crusty, scabbed, or bleeding sore thats not healing.
The
- new growth
- sore thats not healing
- mole thats changing color or shape
Melanoma is a less common but more dangerous form of skin cancer because it can spread easily if not treated. One of the best ways to get a handle on its symptoms is to think of A-B-C-D-E.
- A for asymmetrical. Do you have a mole or spot that seems to be shaped oddly or have two sides that look different?
- B for border. Is the border of your mole or spot jagged?
- C for color. Is the color of your mole or spot uneven or different?
- D for diameter. Is your mole or spot bigger than the size of a pencil eraser?
- E for evolving. Have you noticed your mole or spot changing in an obvious way?
If any of these apply to a mark on your skin, its important to talk with a dermatologist as soon as possible.
Mycosis fungoides
Mycosis fungoides is the most common form of cutaneous T cell lymphoma, a type of blood cancer that involves infection-fighting white blood cells called T cells.
When these cells turn cancerous, they form a red, scaly rash on the skin. The rash can change over time, and it may:
Mycosis fungoides often shows up as an eczema-like rash in areas that typically get little sun exposure.
Actinic keratosis
Actinic keratoses are crusty or scaly pink, red, or discolored bumps that appear on areas of sun-exposed skin, including the:
- face
- scalp
- shoulders
- neck
- backs of your arms and hands
If you have several of them together, they can resemble a rash.
Theyre caused by damage from the suns ultraviolet (UV) radiation. If you dont get actinic keratosis treated, it can turn into skin cancer. Treatments include:
- cryosurgery (freezing them off)
- laser surgery
- scraping off the bumps
Actinic cheilitis
Actinic cheilitis looks like scaly bumps and sores on your lower lip. Your lip might also be swollen and red.
Its caused by long-term sun exposure, which is why it often affects people with lighter skin who live in sunny climates or individuals who spend a lot of time working outside.
Actinic cheilitis can turn into squamous cell cancer if you dont have the bumps removed.
Cutaneous horns
Just as the name suggests, cutaneous horns are hard growths on the skin that look like an animals horns. Theyre made from keratin, the protein that forms skin, hair, and nails.
The horns are concerning because about half the time they grow out of precancerous or cancerous skin sores. Larger, painful horns are more likely to be cancerous.
Youll usually just have one cutaneous horn, but they can sometimes grow in clusters.
Moles (nevi)
Moles, also called nevi, are flat or raised areas of skin. Theyre usually brown or black, but they can also be:
Moles are individual growths, but most adults have between 10 and 40 of them, and they can appear close together on the skin.
Moles are often benign, but in some cases, melanoma the most serious type of skin cancer can begin within a mole.
Seborrheic keratosis
These brown, white, or black bumpy growths form on parts of your body, like your:
They can be tiny or can measure more than an inch across. Although seborrheic keratosis sometimes looks like skin cancer, its actually harmless.
However, because these growths can get irritated when they rub against your clothes or jewelry, you may choose to have them removed.
Basal cell carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that appears as red, pink, or shiny growths on the skin, but it can also appear as dark or gray-colored lesions, especially on individuals with darker skin tones.
Like other skin cancers, its caused by prolonged exposure to the sun.
While basal cell carcinoma rarely spreads, it can leave permanent scars on your skin if you dont treat it.
Merkel cell carcinoma
This rare skin cancer looks like a reddish, purple, or blue-colored bump that grows quickly. It can look like:
- a cyst
- an insect bite
- a sore
- a pimple
Youll often see it on your:
Its more common in people with lighter skin who have had lots of sun exposure, although the exact cause is still not known.
Basal cell nevus syndrome
This rare inherited condition, which is also known as Gorlin syndrome, increases your risk of developing basal cell cancer as well as other types of tumors.
The disease can cause clusters of basal cell carcinoma, especially on areas like your:
A rash is less likely to be cancer if youve taken these steps to protect your skin:
- Try to limit your time in direct sunlight during the hours when the suns UV rays are strongest, which are from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m.
- If you do go outside, apply a broad-spectrum (UVA/UVB) SPF 30 or higher sunscreen to all exposed areas. Reapply after you swim or sweat, or every 2 hours.
- In addition to sunscreen, you can wear sun-protective clothing. You can also wear a broad-brimmed hat and UV-protective sunglasses.
- Try not to use tanning beds.
Check your own skin for any new or changing spots once a month. You may also contact your dermatologist for an annual whole-body check.
In addition to yearly appointments with your dermatologist, its a good idea to regularly check your skin for any moles or red patches that either seem to appear or change over time.
- new, expanding bump or growth on your skin
- sore that continues to bleed or doesnt heal for several weeks
- rough, red, or scaly patch that crusts over or bleeds
- wart-like growth
- mole that seems to be changing color or shape
- mole with irregular borders
When it comes to rashes and spots of all kinds, talk with your doctor if you are unsure.
If you dont already have a dermatologist, your general doctor may refer you to one if they believe you have a suspicious patch or mole on your skin.
During a dermatologist appointment, you will most likely be asked about:
- your symptoms
- whether you remember when the mark first appeared
- whether you have a personal history, or any family history, of skin cancer.
After your dermatologist examines the area in question, they may decide to do a biopsy.
There are a few ways to go about performing a biopsy when it comes to the possibility of skin cancer, but in most cases, your dermatologist will use a local anesthetic to numb the area. Then theyll take a tiny sample of that skin to look at under a microscope.
In very rare cases, your doctor may decide to order an MRI or CT scan of the area if they believe the cancer may have spread below the skin.
How can you tell if a rash is serious?
In many cases, a rash will go away on its own. However, if you notice any of the following symptoms along with a new rash, you should contact your doctor immediately:
- The rash is all over your body.
- You have a fever.
- The rash appears suddenly and spreads quickly.
- The rash becomes red, itches, and blisters.
- The rash is painful.
- The rash looks infected.
What does a cancerous rash look like?
Cancerous rashes, marks, and moles can vary in their appearance. If you notice a red, scaly patch on your skin that itches, cracks, or bleeds and doesnt seem to be healing there is a chance it could be cancerous.
Talking with your doctor or a dermatologist is the best way to figure out if youre dealing with a less serious rash or something that will need to be biopsied.
As a general reminder, if you notice a mark on your skin thats changing shape or color, its important to get a medical opinion as soon as possible.
Are skin cancers itchy?
While many skin cancers may not have any symptoms, some can be itchy.
Basal cell skin cancer can appear as an itchy, reddish patch. Melanoma can also occasionally appear as dark spots or moles that itch. Mycosis fungoides, which is a form of T cell lymphoma, also presents as red, itchy spots on the skin.
Skin rashes are common, and many of them clear up on their own or with over-the-counter medication. However, a very small percentage of skin rashes may be a sign of skin cancer.
If you notice a suspicious mark on your skin that seems to be changing shape or color, you should talk with your doctor or dermatologist as soon as you can. With their help, you will be able to quickly get to the bottom of your issue and receive treatment.
What does an early inflammatory breast cancer rash look like?
Redness or another change in the skin color of the breast, swelling on one side and/or a rash that appears quickly sometimes literally overnight are the hallmark symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer.
But what does that rash actually look like? And how can you distinguish it from other, more benign conditions?
To learn more, we went to Wendy Woodward, M.D., Ph.D., a radiation oncologist and researcher who specializes in the treatment of inflammatory breast cancer.
What does an inflammatory breast cancer rash look like?
Thats kind of hard to say, because not everyones rash looks the same. And, it doesnt always look like a rash. Sometimes, you can just see the breast skin pores very clearly because they look exaggerated due to swelling. Or, theres redness or some other type of discoloration of one breast.
The rash associated with inflammatory breast cancer can also vary in appearance based on someones skin tone. It may look dark or even purple on some women, rather than red. But theres not a defining skin change thats the same for everybody. And, no matter how early a rash is diagnosed as inflammatory breast cancer, it is always considered at least stage III.
What characteristics distinguish an inflammatory breast cancer rash from other kinds?
Speed is one factor. Inflammatory breast cancer is quite aggressive, and it can develop very, very quickly. So, if you notice a marked change in the size of your breast or in its color or texture over a few weeks or even a few days or hours you should get it evaluated right away.
In addition, though some women describe the rash as starting out small or even resembling a bug bite it often involves most of the breast within a very short time frame. So, a spreading rash deserves prompt attention, too.
Are there any other conditions that can cause rashes on the breast?
Yes. Mastitis is the top one. Its fairly common during breastfeeding, so many people tend to assume that inflammatory breast cancer is just an infection. It gets mistaken for mastitis and abscesses a lot because most health care providers have never seen inflammatory breast cancer before. They tend to err on the side of the rash being caused by something more benign.
The number of people diagnosed with inflammatory breast cancer each year is incredibly small. Its a drop in the bucket, compared to other types of breast cancer. And most people who notice changes in their breasts will not ultimately have breast cancer.
By the time patients get to MD Andersons specialized Inflammatory Breast Cancer Clinic, though, theyve often already gone through multiple rounds of antibiotics with no improvement.
Have there been any advances in the diagnosis of inflammatory breast cancer, based on rashes?
Yes. Were working on two different projects right now.
One is an update of the MD Anderson cancer algorithm to help patients obtain a faster diagnosis. If the changes theyve noticed are enough to point to inflammatory breast cancer, theyll be able to use this algorithm to back up their request for additional imaging or a breast biopsy.
That way, if a doctor says, OK, here are some more antibiotics, patients can say, Wait. Shouldnt we try to rule this out first? and show them the MD Anderson algorithm. A lot of doctors think of a breast biopsy as a really big step. But in this case, its not. Its just the right thing to do.
Were also in the very early stages of developing of an app that would let patients take a picture of their own breast, upload it and use artificial intelligence to compare it to photos of both healthy breasts and those from patients with confirmed inflammatory breast cancer diagnoses. The hope is to give patients a gauge to determine whether their rash is something to be concerned about and doctors a tool to make a diagnosis right away.
Is there anything else people should know about inflammatory breast cancer rashes?
Yes. Sometimes, it can be hard to distinguish non-inflammatory breast cancer from inflammatory breast cancer, since both can cause redness of the breast and skin changes that might be missed.
But if you notice really rapid changes in one or both of your breasts, try to be seen by a doctor within two weeks. While a short course of antibiotics is not unreasonable when the suspicion of inflammatory breast cancer is low, dont be afraid to ask for breast imaging or a biopsy if your symptoms dont fully resolve in less than two weeks. If your condition gets better before the results come in, great. But if not, youll be that much closer to a diagnosis.
Request an appointment at MD Anderson online or by calling 1-877-632-6789.