What food can I give my dog with skin allergies

The Best Foods for Dogs With Allergies
Humans arent the only ones with allergiesour dogs can get them, too. Canine allergies can lead to numerous skin conditions that can be frustrating to manage. These allergies can be due to environmental causes or from the food our dogs eat.
Key Takeaways
- Dogs can be allergic to foods like beef, chicken, lamb, wheat, soy, eggs, corn, and nuts.
- Allergy tests for dogs are not reliable.
- The only proven way to tell what your dog is allergic to is to change their protein source or perform an elimination diet trial.
The most common symptoms of dog food allergies include:
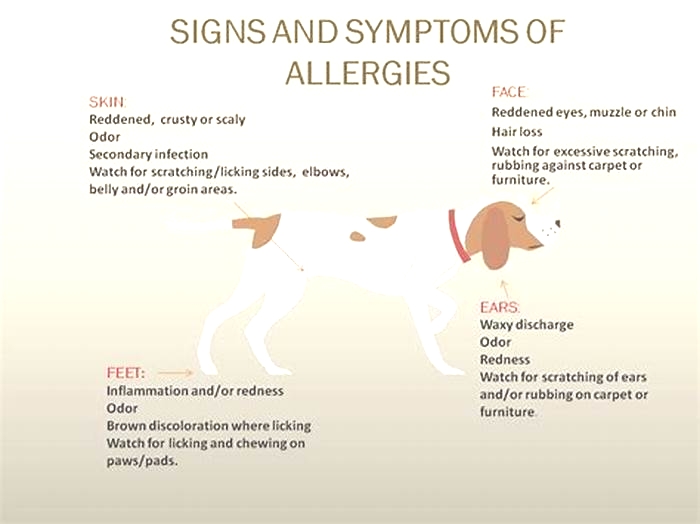
Redness of the skin of the inner ears
Itchiness of the ears (chronic scratching of the ears or shaking of the head)
Ear hematomas
Chronic thickening of the ears
Chronic ear infections
Redness and itchiness of the feet or in between toes (foot chewing)
Chronic pododermatitis
Patchy hair loss along the neck and trunk
Chronic skin infections (with bacteria or yeast) that never seem to clear up
Skin issues are the most common dog food allergy symptoms. These are mostly seen as an allergic reaction to the proteins absorbed in food.
The reaction leads to the release of immune cells, which can cause weakening of the bonds between the skin cells, resulting in a weakening of the skin barrier. This change in the skin barrier leads to redness and itchiness, and it makes the skin more susceptible to infection with normal bacteria and yeast.
The most affected areas are the ears, paws, around the eyes, and sometimes the trunk (torso) and limbs.
What Are Common Dog Food Allergens?
The most common proteins dogs are allergic to are beef, chicken, lamb, and wheat. Other less common causes of dog food allergies include soy, eggs, corn, and nuts.
Dogs cannot be tested for food allergies like people can, as the available testing is unreliable. The only proven way to tell what your dog is allergic to is to change their protein source or perform an elimination diet trial.
During an elimination diet trial, you eliminate all proteins your dog has been exposed to for two to three months. This gives the body enough time to completely eliminate the old protein sources and heal from the chronic allergy stimulation.
How To Help a Dog With Food Allergies
An elimination diet trial withhydrolyzed foodis the best way to treat and diagnose a dog food allergy. Its easiest to start with a prescription diet, such asHills z/dorRoyal Canin Hydrolyzed Protein. Theseveterinary dietshave proteins that are too small to be recognized by the immune system.
An elimination diet trial takes approximately two to three months to complete. This time is necessary for the old proteins to leave the dogs system. Additionally, the dog must be on the diet long enough to see a difference from the previous food.
The most common mistake pet parents make is not waiting long enough before calling it quits on the diet trial. Changing what your dog is eating for just a week or two will not give you complete results, so taking the proper amount of time to test food and treats is crucial.
Another common mistake: feed a dog anything other than the elimination diet. During a diet trial, pets cannot have any table scraps or treats (unless the elimination diet has a compatible treat option).
Changing what your dog is eating for just a week or two will not give you complete results, so taking the proper amount of time to test food and treats is crucial.
If the symptoms do not resolve after two or three months on the hydrolyzed elimination diet trial, your dog most likely has some type of environmental allergen. Or something else is causing the problem, such as an autoimmune condition.
If you get a good response from the trial, try to feed your dog a new protein source, such as venison, fish, or kangaroo. If they are going to react to these proteins, you should notice a mild reaction starting within two weeks. If their allergy symptoms return, stop the new protein source and go back to the hydrolyzed food.
Try adding one protein at a time every two to four weeks. If your dog reacts, stop and keep things steady for another two weeks before trying a different protein.
Contact your veterinarian before starting any diet trial to get a prescription for a hydrolyzed diet. Its also important to see your veterinarian to make sure your pet doesnt have any concurrent infections, which can be common because of the disturbed skin barrier caused by the allergic reaction. Infections can look the same as dog food allergy symptoms, so you must make sure to clear all infections during the food elimination trial.
During the trial, remember:
Make sure the prescription treats and food are all that you are feeding your pet. You cant feed human food or regular pet treats with a food trial, as it can introduce the allergens youre trying to eliminate.
Alwaysintroduce a dog to a new diet slowlyto avoid stomach upset or diarrhea.
The Best Dog Food for Allergies
Hydrolyzed Dog Foods
Hydrolyzed foods are the best dog food for allergies because the proteins are broken down into pieces that are so small the body cant recognize them. Some of these foods include:
Novel Protein Foods
Novel protein diets include proteins that your dog has not been introduced to before, such as duck, fish, venison, and kangaroo. Some examples of novel protein diets are:
Foods for Puppies With Allergies
While its rare for puppies to have food allergies, there are some documented cases in pups as young as 6 months old. If you think your puppy may have a food allergy, lamb and rice formulas, such asPurina Puppy Lamb & Rice Formula, would be a good place to start for a novel protein.
If allergies are severe and your vet recommends a hydrolyzed diet, Royal Canin Hydrolyzed Protein does come in a puppy formulation.
WRITTEN BY
Robyn Gallucci, DVMVeterinarian
Dr. Gallucci started her career in veterinary medicine as a kennel assistant in high school and began training as a technician in college....
Skin Disease Due to Food Allergies in Dogs
Dermatologic Food Reactions in Dogs
Dermatologic food reactions are non-seasonal reactions which occur following ingestion of one or more allergy causing substances in an animals food. The physical reaction is frequently excessive itchiness, with resultant excessive scratching at the skin.
While the pathogenesis of these reactions is not fully understood, immediate reactions and delayed reactions to food are thought to be due to a hypersensitive immune response. On the other hand, food intolerance is a non-immunologic idiosyncratic reaction due to the metabolic, toxic or pharmacologic effects of the offending ingredients. Since it is not easy to distinguish between immunologic and idiosyncratic reactions, any negative response to food is generally referred to as an adverse food reaction.
Symptoms and Types
- Non-seasonal itchiness of any body location
- Poor response to anti-inflammatory doses of glucocorticoids generally suggests food hypersensitivity
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Excessive gut sounds, passing of gas, and frequent bowel movements
- Malassezia dermatitis (fungal skin infections), pyoderma (bacterial skin infections), and otitis externa (inflammation of the outer ear)
- Skin plaques broad, raised flat areas on the skin
- Pustules pus-containing raised skin inflammations
- Erythema redness of the skin
- Crusts dried serum or pus on the surface of a ruptured blister or pustule
- Scale flakes or plates of dead skin on the skin's surface
- Self-induced baldness due to scratching
- Abrasions/sores on the skin due to scratching
- Leathery, thick, bark-like skin
- Hyperpigmentation darkening of the skin
- Hives swollen or inflamed bumps on the skin
- Giant wheals (elongated marks) on the skin
- Pyotraumatic dermatitis infection of the skin wounds due to scratching excessively, and bacteria entering the wounds
Causes
- Immune-mediated reactions result of the ingestion and subsequent presentation of one or more glycoproteins (allergens) either before or after digestion; sensitization may occur as the food passes into the intestine, after the substance is absorbed, or both
- Non-immune (food intolerance) reactions result of ingestion of foods with high levels of histamine (an antigen known to cause immune hypersensitivity) or substances that induce histamine either directly or through histamine-releasing factors
- It is speculated that in juvenile animals, intestinal parasites or intestinal infections may cause damage to the intestinal mucosa, resulting in the abnormal absorption of allergens and subsequent sensitization to some ingredients
Diagnosis
Your veterinarian will perform a complete physical exam on your dog, including a dermatological exam. Non-food causes of dermatologic disease should be ruled out. Your veterinarian will order a blood chemical profile, a complete blood count, a urinalysis and an electrolyte panel to rule out other causes of disease. You will need to give a thorough history of your dog's health, onset of symptoms, and possible incidents that might have preceded this condition, especially regarding any changes in diet, and any new foods added to your dog's diet, even if temporary.
Food elimination diets are advised for dogs thought to be suffering from adverse food reactions. These diets typically include one protein source and one carbohydrate source to which the dog has had limited or no previous exposure to. A clinical improvement may be seen as soon as four weeks into the new diet, and maximum alleviation of clinical signs may be seen as late as thirteen weeks into the food elimination diet.
If your dog improves on the elimination diet, a challenge should be performed to confirm that the original diet was the cause of disease and to determine what ingredient in the original diet triggered the adverse reaction.
Challenge: feed your dog with the original diet. A return of the signs confirms that something in the diet is causing the signs. The challenge period should last until the signs return but no longer than ten days.
If the challenge confirms the presence of an adverse food reaction, the next step is to perform a provocation diet trial: going back to the elimination diet, begin by adding a single ingredient to the diet. After waiting a sufficient amount of time for the ingredient to prove either agreeable or adverse, if there is no physical reaction, move on to adding the next ingredient to your dog's diet. The provocation period for each new ingredient should last up to ten days, less if signs develop sooner (dogs usually develop signs within 12 days). Should symptoms of an adverse reaction develop, discontinue the last added ingredient and wait for the symptoms to subside before moving forward to the next ingredient.
The test ingredients for the provocation trials should include a full range of meats (beef, chicken, fish, pork, and lamb), a full range of grains (corn, wheat, soybean, and rice), eggs, and dairy products. The results of these trials will guide your selection of commercial foods, based on those that do not contain the offending substance(s).
[video]
Treatment
Avoid any food substances that caused the clinical signs to return during the provocation phase of the diagnosis. Antibiotics or antifungal medications may be prescribed by your veterinarian if secondary pyodermas or Malassezia infections are taking place.
Living and Management
Treats, chewable toys, vitamins, and other chewable medications (e.g., heartworm preventive) that may contain ingredients from your dog's previous diet must be eliminated. Make sure to read all ingredient labels carefully. If your dog spends time outdoors you will need to create a confined area to prevent foraging and hunting, which can alter the test diet. All family members will need to be made aware of the test protocol and must help keep the test diet clean and free of any other food sources. Cooperation is essential to successful treatment of this disorder.
Food allergies in dogs
Treatment
If the food trial confirms that your dog has a food allergy, your vet might recommend feeding your dog their new diet for life, as long as its a complete food that contains all the necessary nutrients. Your dog shouldnt have any other food or treats at all. Keep all human food and other pet food safely out of reach.
Once your dog is settled without symptoms on their special diet, you can try adding ingredients back into their food (one at a time) to try and find out what they are allergic to. If your dog doesnt show any symptoms, this is a safe food. Alternatively, if your dogs symptoms come back after eating a certain food, its likely they are allergic to it. This will help you select a dog food that only contains safe foods. If you want to do this you should follow your vets advice.
Some dogs with a food allergy will also have allergies to things in the environment, this may cause atopic dermatitis (allergic skin disease). In this case, they might improve a bit on a special diet but they may need other treatments as well to help keep their skin symptoms controlled.