What happens to untreated yeast infection in dogs

Yeast Dermatitis (Malassezia) in Dogs: Signs, Symptoms, Treatments
Humans and dogs both uncomfortable when the weather gets hot and humid. That combination creates the perfect environment for yeast to grow and multiply on your dogs skin. An overgrowth of yeast can lead to a condition called yeast dermatitis in dogs or Malassezia dermatitis.
Dogs with yeast dermatitis tend to have itchy and inflamed skin, and they may be very uncomfortable. Heres what you need to know about Malassezia in dogs, including causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment.
What Causes Yeast Dermatitis in Dogs?
Malassezia pachydermatis is a yeast (which is also a fungus). Its a normal inhabitant of a dogs skin, ears, and mucous membranes. A problem only occurs when theres too theres too much of this yeast, leading to secondary issues like a yeast infection, says Dr. Amy Attas, VMD of New York-based practice City Pets. Yeast dermatitis isnt a contagious disease, so a dog cant get Malassezia from another dog.
There are two main reasons why dogs develop yeast dermatitis: factors in the environment and factors in the patient. Being in hot and humid weather, as well as going for a walk on a rainy day, can increase the likelihood of a dog developing a yeast infection. In these circumstances, dirt and moisture can get trapped between their toes or skin folds, creating an ideal breeding ground for yeast. In addition to environmental factors, dogs may have some kind of issue that helps the yeast go from colonizing i.e., normal numbers to becoming infected, she says.
The most common cause of yeast dermatitis in dogs is allergies, including food sensitivities. Dogs with allergies tend to get a lot of yeast infections on their feet, their skin, and in their ears, she says. Another cause of yeast dermatitis in dogs may be problems with a dogs immune system. For example, if a dog has been on long-term antibiotics, their immune systems may be weaker, making the dog more prone to contracting an illness. In addition to treating harmful bacteria, antibiotics can also kill some of the ones that are keeping the Malassezia in check, Dr. Attas says. Yeast are opportunistic organisms that are going to take over if the patient has issues.
Symptoms Yeast Dermatitis in Dogs
Too much yeast in a particular area can cause the skin or tissue inside the ear to become inflamed. When this happens, dogs get uncomfortable and may seek relief by rubbing or scratching the affected area. Once a dog starts to get itchy, they can create an environment for a secondary infection in the ears or on the skin, Dr. Attas explains. Here are symptoms to look for in a dog with Malassezia:
- Itchy or inflamed skin
- Smelling like sour milk
- Coat that feels greasy to the touch
- Hair loss
- Scaly skin
- Skin turning black or become thickened if left untreated
- Dark brown, greasy discharge with a foul smell
Diagnosing Yeast Dermatitis in Dogs
Sometimes, because of the sour milk odor, a veterinarian can tell that your dog has Malassezia dermatitis just by smelling them. But before administering treatment, theyll confirm the diagnosis by collecting a sample of the dermatitis. There are several ways they can obtain a sample for testing.
If theres abundant discharge in the ears or on the skin, you can use a Q-tip and make a very thin preparation on a slide, Dr. Attas says. Then you can look at it under the microscope with special staining. Another painless option is doing an acetate tape preparation, which involves taking a piece of tape, pressing it against the area that looks infected, and peeling off the tape. The vet will then place the tape on a microscopic slide for further inspection.
A third way to get a sample is with a skin scraping. The vet will take a scalpel blade and gently take off the top layer of cells, which doesnt hurt the dog. It doesnt bleed and that gives an abundant supply of organisms to check under the microscope, she says.
If necessary, your vet may conduct a diagnostic test called a punch biopsy to see if theres a lot of yeast in an area, she explains. The vet might need to examine a full layer of skin to make a proper diagnosis and come up with a treatment plan. A punch biopsy involves using a sharp cutting tool to remove a small, tube-shaped piece of skin for microscopic examination. In most cases, this test isnt necessary.
Treatments for Yeast Dermatitis in Dogs
Typically, the treatment for yeast dermatitis in dogs involves topical agents (meaning you apply them directly to the body), like medicated dog shampoo, leave-in conditioner, and mousse. If your dog has a skin infection and Malassezia is the only yeast present, your vet may recommend using an antiseptic cleanser with an ingredient like chlorhexidine or a topical cream or spray with ingredient like ketoconazole. Yeast dermatitis may take a bit longer to treat than a bacterial infection.
Depending on how bad the infection is, you may need to bathe your dog one to three times a week, Dr. Attas says. If a dog is really greasy, Dr. Attas suggests using a degreasing cleanser for dogs (with an ingredient to cut through the grease like benzoyl peroxide) in combination with an anti-yeast shampoo for dogs. Using a degreasing cleanser helps ensure that the anti-yeast shampoo is making good contact with the skin.
The decision to use topicals is made based on how much of the body is affected and where on the body it is, Dr. Attas explains. For example, you wouldnt want to use shampoo for a yeast infection around your dogs eyes. In such cases, the vet might recommend treating the infection with oral medication.
Your vet might also prescribe oral medications if your dogs infection isnt improving or if its making them very uncomfortable. These oral antifungals for dogs include ketoconazole, itraconazole, fluconazole, and terbinafine. Theyre given orally and are metabolized through the liver, she says. If a dog needs to be on them for a prolonged period of time, well need to monitor their blood work.
Yeast Dermatitis: Prognosis and Prevention
To avoid chronic Malassezia infections, your vet may recommend early treatment. They may also recommend taking steps to keep yeast in check.
Breeds Predisposed to Yeast Dermatitis
Some dog breeds, like the West Highland White Terrier, Cocker Spaniel, Poodle, and Dachshund, are predisposed to developing yeast dermatitis. Other dogs that are prone to allergies and yeast infections are those with long, floppy ears or skin folds, great places for fungus to hide. They tend to be the same breeds that are overrepresented for allergies, Dr. Attas says. Thats the key thing here, if we dont address allergies, were not going to get these dogs better.
These dogs may also recover from yeast dermatitis, then contract another infection if the cause of the underlying allergy isnt addressed. So if your dog has allergies and recurrent yeast infections, be sure to talk to your vet.
Keep Your Dog Clean and Dry
Water can get into the ear canal when your dog goes for a swim. Then, if they have a floppy ear, weve just created a warm and moist environment thats very inviting to these organisms, Dr. Attas says. After your dog has a bath or goes swimming, make sure to dry their ears. You can use a cotton ball or sprinkle on an ear-drying agent that you put in the ear, rub around, and wipe clean.
Overweight dogs may be prone to allergies and yeast infections, as will dogs with long, floppy ears and dogs with lots of skin folds. Those folds tend to get moist and warm, so keeping them clean and dry will help prevent yeast from coming back, Dr. Attas says.
Bulldogs may be at higher risk of yeast on their feet because there isnt much space between their toes. If they go for a walk in the rain or mud, be sure to clean and dry their feet afterward.
Dr. Attas reminds owners that yeast is an organism that loves humidity. So once youve dealt with allergies, yeast dermatitis and infections will tend to be less of a problem. Cleaning skin folds and drying your dogs ears will make a less welcoming environment for yeast organisms and relieve some of your dogs discomfort.
Yeast Infections in Dogs: What to Know
Yeast infections in dogs are common, especially in certain breeds or dogs with underlying conditions and compromised immune systems. While they can occur anywhere on the skin, they are often seen in your dogs ears. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing serious complications. Heres what to know about yeast infections in dogs to keep your dog healthy.
What Causes a Yeast Infection in Dogs?
Yeast is a live, single-celled microorganism classified as a member of the fungus kingdom. Its normally found on every dogs skin, but in small amounts. A yeast infection occurs when a substantial amount of yeast excessively builds up in one area.
Yeast infections often occur if there is an underlying medical condition, such as food sensitivities, environmental factors, or parasites, such as fleas, which can cause allergies, as well as the dermatological condition seborrhea. Bacterial infections or underlying hormonal problems may also throw the skins defenses off-balance. In the case of yeast infections of the ear, the most common causes are water or debris trapped in the ear or food sensitivities. Yeast infections of the ear could also be caused by underlying mechanical issues such as damage to the eardrum, a polyp, or even a mass or tumor in the ear canal.
Are Some Breeds More Susceptible to Yeast Infections?
Certain dog breeds are thought to be genetically predisposed to developing yeast infections. These breeds include the West Highland White Terrier, Basset Hound, Cocker Spaniel, Silky Terrier, Australian Terrier, Maltese, Chihuahua, Poodle, Shetland Sheepdog, Lhasa Apso, and Dachshund.
Dogs with floppy ears who swim often, such as Golden Retrievers and Labrador Retrievers, are more likely to get yeast infections. Breeds such as Miniature Schnauzers, Bichon Frise, and Shih Tzu are also more susceptible to infections because the thick hair in their ear canals hampers the airflow necessary to keep ears dry.
Any dog with allergies is also more likely to develop yeast infections.
Types of Yeast Infections in Dogs and How to Recognize Them
Yeast Infections in Ears
The ear canal of a dog is L-shaped, dropping down and toward the head. This dark, warm, moist environment is the perfect setting for a yeast infection to thrive. The two types of yeast most often found in a dogs ears are Candida and Malassezia.
Yeast infections can occur in any part of the dogs ear. A dog with a yeast infection in their ear may exhibit these symptoms:
- Scratching and digging at the ear
- Rubbing the head on the floor, walls, or furniture
- Excessive shaking of the head
- Musty odor
- Brown, yellow, or bloody discharge
- Crusted skin or fur on the ear flap
- Swelling and redness
- Hair loss around the base of the ear
Early diagnosis and treatment of a yeast infection in the ears are critical before it spreads deeper. If a yeast infection spreads deeper into the ear, it can cause serious pain and complications, such as loss of hearing, vestibular imbalance, or neurological damage.
Yeast Infections on Paws
A dogs paws are susceptible to yeast infections because they encounter wet, dirty ground, which means moisture and dirt are likely to be trapped between the toes and pads. Contact with grass and weeds can also trigger allergies or result in cuts and scratches. Dogs are likely to lick their irritated paws, which doesnt help, instead adding even more moisture.
If your dog has a yeast infection on the paws, you may see the following symptoms:
Excessive licking and chewing of the feet
- Redness and irritated skin
- Brown discharge in nailbeds
- Pink salivary staining on the hair around the paws
- Hair loss
There could be many reasons a dog excessively licks their paws, including anxiety, boredom, injury, parasites, bacteria, or allergies, including food sensitivities. Early examination, diagnosis, and appropriate treatment by a veterinarian can relieve discomfort and prevent complications. This is made using a combination of their medical history and diagnostic swabs of the debris or accompanying cells.
Yeast Infections on Skin
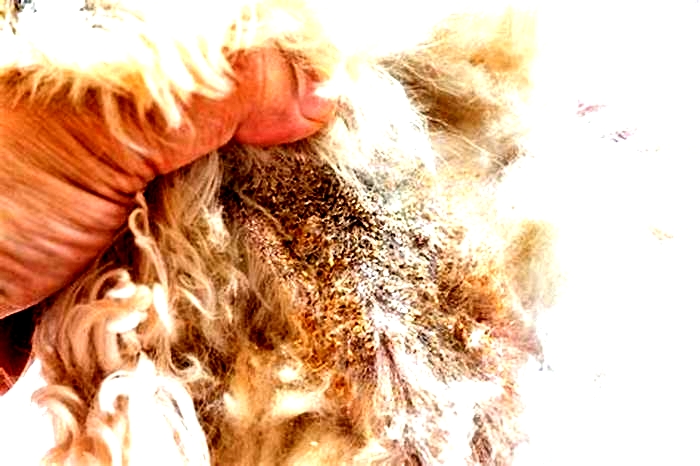
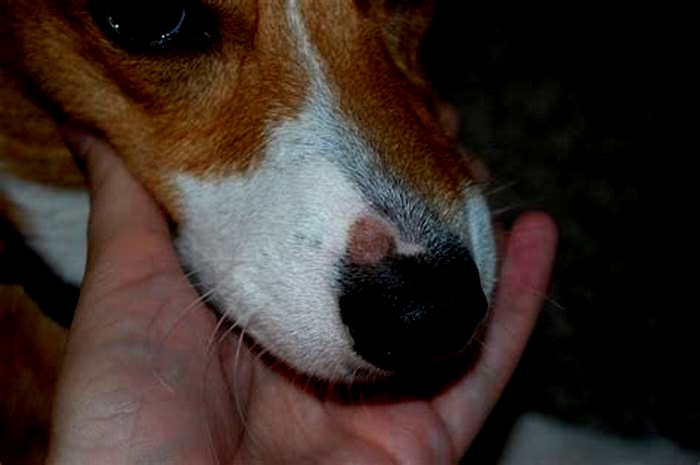
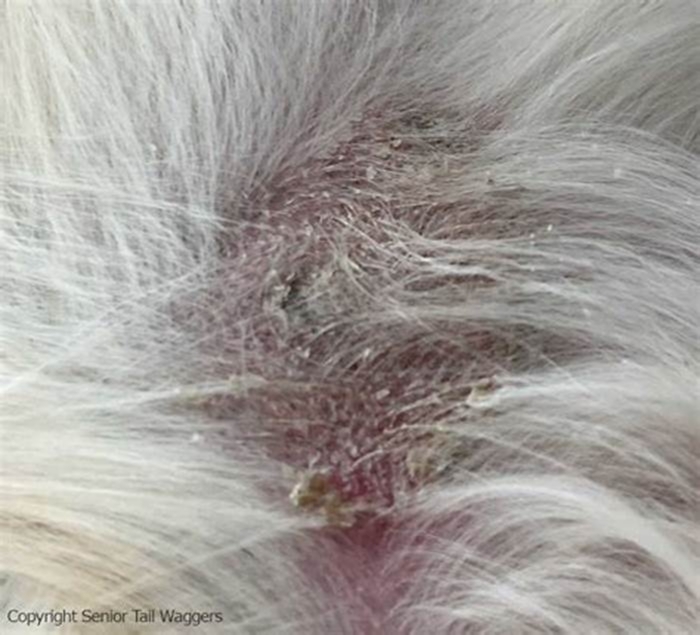
Yeast dermatitis, a skin inflammation caused by yeast infections, can spread to any area of a dogs skin. But its most likely to occur at the site of a rash or wherever there are skin folds that can trap moisture. Wrinkly breeds, such as the Chinese Shar-Pei, are especially vulnerable.
Symptoms of yeast infections of the skin include:
- Intense itching
- Red, irritated, inflamed skin
- Greasy, crusty, or flaky patches
- Thickening (elephant-like) skin
- Darker skin color
- Hair loss
- Musty smell
Although a yeast infection of the skin may start in a very specific area, if left untreated, it can spread and affect the entire body, including the dogs face and mouth. Often, there may be a secondary bacterial infection accompanying the yeast infection.
How to Treat Yeast Infections in Dogs
Depending on how deep in the ear canal a yeast infection is, the treatment will vary. The veterinarian will prescribe a topical antifungal cream for an infection in the outer ear. An infection of the middle ear may require antifungal drops or oral medication. The vet is likely to recommend a thorough cleaning of the ear and possibly ongoing treatment with ear-drying solutions.
Yeast infections on the paws may require treatment with a disinfectant spray to kill germs, as well as daily application of a topical antifungal lotion or spray. It may also be necessary to use an Elizabethan collar to keep the dog from licking the paws so they can stay dry while they heal.
Skin infections may require topical and oral treatment. Cleansing shampoos may clean up the greasy skin. Your vet may recommend using a medicated, antifungal shampoo and leaving it on the dogs skin for about 10 minutes. Bathing may need to be repeated for up to 12 weeks. The veterinarian will also prescribe an antifungal medication, as well as an antibiotic, to treat any bacterial skin infection that may occur along with yeast dermatitis.
How to Prevent Yeast Infections in Dogs
The good news is that yeast infections in dogs are not contagious to other dogs or humans. The most important thing to remember to prevent yeast infections is to keep the area clean and dry.
Too much moisture is a common cause of ear infections, so thoroughly drying your dogs ears after swimming and bathing can prevent moisture build-up. If your dog has a skin rash, musty smell, or is scratching or licking excessively, taking them to the veterinarian can prevent an infection from spreading and becoming more serious.
The prognosis for yeast infections is good when you follow the treatments your veterinarian gives you. Its important to understand that unless an underlying problem such as allergies, hypothyroidism, or seborrhea is controlled, a yeast infection is likely to come back.