Why do dogs get skin infections
Skin Infections in Dogs
What Are Skin Infections in Dogs?
Skin infections are conditions that are caused by infectious organisms such as bacteria, fungi, or parasites. All areas of skin can be affected, including inside the ears and nose, as well as the hair and nails.
The severity of the disease depends on the type of infection and can vary from very mild to painful and itchy. Some organisms that cause skin infections are transmissible (or contagious), which means the infection can be passed to another mammal through direct contact or the environment. There are also infections that are caused by organisms that normally live on the skin and are not considered contagious.
Types of Skin Infections in Dogs
Bacterial
Fungal
Parasitic
Viral
Symptoms of Skin Infections in Dogs
Redness
Bumps or raised areas of the skin
Itchiness (you may see your dog scratching, licking, and/or chewing the skin)
Scales or flakes
Crusts or scabs
Hair loss (alopecia)
Oozing or discharge (blood, pus, clear)
Skin color changes (darker or lighter)
Causes of Skin Infections in Dogs
There are many causes of skin infections in dogs. Some infections are primary infectionsan infection directly caused by an infectious organism. Other infections are secondary infections and occur because of an underlying disease process that triggers an infection.
Primary Infection
Scabies is an example of a primary parasitic skin infection. Dogs acquire scabies by direct contact with an infected animal. The scabies mite then causes the clinical signs associated with the disease. Ringworm is an example of a primary fungal infection and is acquired due to contact with infected individuals or an infected environment, including soil.
Secondary Infection
A common example of a secondary skin infection is one due to skin allergies. The allergies cause inflammation of the skin, which then provides an environment favorable to organism growth. Bacteria or fungi that normally live on the skin are then able to multiply, leading to a bacterial or fungal skin infection.
How Veterinarians Diagnose Skin Infections in Dogs
There are several basic skin tests that are useful in diagnosing a majority of skin infections. The most common ones are:
Skin scrapes: A dull scalpel blade is used to scrape the top layer of the skin; effective for finding skin parasites like demodex.
Skin cytology: A sample is collected by pressing a microscope slide directly to the skin lesion or via a needle and syringe and then looked at under the microscope for bacteria, fungi, or abnormal skin cells.
Tape preps: Clear tape is used to collect a sample of hair or skin to find bacteria, fungi, or parasites when viewed under the microscope.
Cotton swabs: A cotton swab is used to collect a sample, most often from inside the ear, to diagnose bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infections.
Cultures: A sample of skin, hair, or discharge is collected onto a growth plate to look for bacterial or fungal growth over time. This test can also be used to learn which antimicrobial medication is best to treat the infection.
Treatment of Skin Infections in Dogs
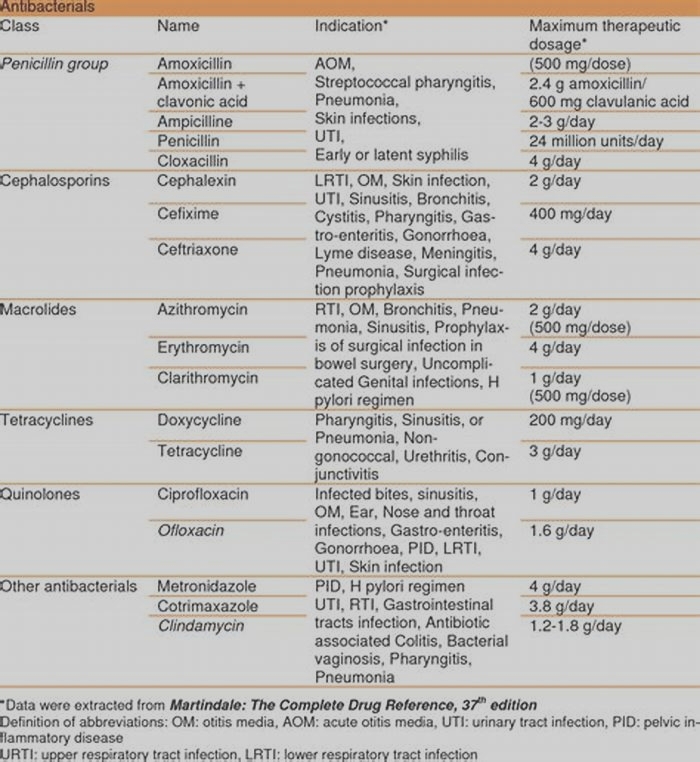
The treatment of a skin infection depends on the type of infection, the location of the infection, and the condition of the dog. Bacterial skin infections are treated with oral (by mouth) antibiotics, and/or topical products such as medicated shampoos, conditioners, sprays, and ointments. Common products include:
Fungal infections are treated similarly, with antifungal medications, and parasites are treated with antiparasitic medications.
To help the skin heal and to prevent future infections, other treatments are used to support healthy skin. For example, when treating an ear infection, special ear cleaners are used in addition to the antimicrobial medication. Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation is another treatment used to help resolve and prevent infections. Prevention is often the best medicine and regular bathing and grooming can be helpful for not only treating skin infections but also preventing them from occurring in the first place.
For secondary skin infections, it is important to treat the primary cause of the secondary infection. Skin allergies, for example, frequently require medications to reduce inflammation and allergic reactions. Treating a skin infection without treating the allergy will likely lead to another infection. Food allergies require special diets to reduce skin inflammation. If a food allergy is suspected, your vet will work with you to determine an appropriate food trial,to slowly remove certain ingredients and introduce possible allergies to determine the culprit.
Recovery and Management of Skin Infections in Dogs
The time it takes to treat a skin infection depends on the type of infection, the ability to treat primary causes of the infection, and the severity of disease. Sometimes the most difficult part of the treatment is sticking with treatments for as long as needed.
Some skin infections can be difficult to treat because of antimicrobial resistance. Antimicrobial resistance occurs over time, when microbes develop defenses against our medications, making those medications ineffective. In those cases, treatment can take longer and may require further testing.
Infections can resurface, especially if the primary cause of the infection has not been treated or resolved. Dogs with chronic conditions such as allergies or other diseases are more likely to have repeat infections.
Managing skin infections successfully can be complicated, time consuming, and expensive. Following your veterinarians recommendations closely and being patient during the treatment period is important for resolving the infection and preventing recurrence in your pup.
Featured Image: iStock.com/Sergeeva
WRITTEN BY
Dr. Rania GollaknerVeterinarian
Rania Gollakner received her Doctor of Veterinary Medicine degree in 2010 and a Master of Public Health in 2017. She practiced companion...
Yeast Infections in Dogs: What to Know
Yeast infections in dogs are common, especially in certain breeds or dogs with underlying conditions and compromised immune systems. While they can occur anywhere on the skin, they are often seen in your dogs ears. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing serious complications. Heres what to know about yeast infections in dogs to keep your dog healthy.
What Causes a Yeast Infection in Dogs?
Yeast is a live, single-celled microorganism classified as a member of the fungus kingdom. Its normally found on every dogs skin, but in small amounts. A yeast infection occurs when a substantial amount of yeast excessively builds up in one area.
Yeast infections often occur if there is an underlying medical condition, such as food sensitivities, environmental factors, or parasites, such as fleas, which can cause allergies, as well as the dermatological condition seborrhea. Bacterial infections or underlying hormonal problems may also throw the skins defenses off-balance. In the case of yeast infections of the ear, the most common causes are water or debris trapped in the ear or food sensitivities. Yeast infections of the ear could also be caused by underlying mechanical issues such as damage to the eardrum, a polyp, or even a mass or tumor in the ear canal.
Are Some Breeds More Susceptible to Yeast Infections?
Certain dog breeds are thought to be genetically predisposed to developing yeast infections. These breeds include the West Highland White Terrier, Basset Hound, Cocker Spaniel, Silky Terrier, Australian Terrier, Maltese, Chihuahua, Poodle, Shetland Sheepdog, Lhasa Apso, and Dachshund.
Dogs with floppy ears who swim often, such as Golden Retrievers and Labrador Retrievers, are more likely to get yeast infections. Breeds such as Miniature Schnauzers, Bichon Frise, and Shih Tzu are also more susceptible to infections because the thick hair in their ear canals hampers the airflow necessary to keep ears dry.
Any dog with allergies is also more likely to develop yeast infections.
Types of Yeast Infections in Dogs and How to Recognize Them
Yeast Infections in Ears
The ear canal of a dog is L-shaped, dropping down and toward the head. This dark, warm, moist environment is the perfect setting for a yeast infection to thrive. The two types of yeast most often found in a dogs ears are Candida and Malassezia.
Yeast infections can occur in any part of the dogs ear. A dog with a yeast infection in their ear may exhibit these symptoms:
- Scratching and digging at the ear
- Rubbing the head on the floor, walls, or furniture
- Excessive shaking of the head
- Musty odor
- Brown, yellow, or bloody discharge
- Crusted skin or fur on the ear flap
- Swelling and redness
- Hair loss around the base of the ear
Early diagnosis and treatment of a yeast infection in the ears are critical before it spreads deeper. If a yeast infection spreads deeper into the ear, it can cause serious pain and complications, such as loss of hearing, vestibular imbalance, or neurological damage.
Yeast Infections on Paws
A dogs paws are susceptible to yeast infections because they encounter wet, dirty ground, which means moisture and dirt are likely to be trapped between the toes and pads. Contact with grass and weeds can also trigger allergies or result in cuts and scratches. Dogs are likely to lick their irritated paws, which doesnt help, instead adding even more moisture.
If your dog has a yeast infection on the paws, you may see the following symptoms:
Excessive licking and chewing of the feet
- Redness and irritated skin
- Brown discharge in nailbeds
- Pink salivary staining on the hair around the paws
- Hair loss
There could be many reasons a dog excessively licks their paws, including anxiety, boredom, injury, parasites, bacteria, or allergies, including food sensitivities. Early examination, diagnosis, and appropriate treatment by a veterinarian can relieve discomfort and prevent complications. This is made using a combination of their medical history and diagnostic swabs of the debris or accompanying cells.
Yeast Infections on Skin
Yeast dermatitis, a skin inflammation caused by yeast infections, can spread to any area of a dogs skin. But its most likely to occur at the site of a rash or wherever there are skin folds that can trap moisture. Wrinkly breeds, such as the Chinese Shar-Pei, are especially vulnerable.
Symptoms of yeast infections of the skin include:
- Intense itching
- Red, irritated, inflamed skin
- Greasy, crusty, or flaky patches
- Thickening (elephant-like) skin
- Darker skin color
- Hair loss
- Musty smell
Although a yeast infection of the skin may start in a very specific area, if left untreated, it can spread and affect the entire body, including the dogs face and mouth. Often, there may be a secondary bacterial infection accompanying the yeast infection.
How to Treat Yeast Infections in Dogs
Depending on how deep in the ear canal a yeast infection is, the treatment will vary. The veterinarian will prescribe a topical antifungal cream for an infection in the outer ear. An infection of the middle ear may require antifungal drops or oral medication. The vet is likely to recommend a thorough cleaning of the ear and possibly ongoing treatment with ear-drying solutions.
Yeast infections on the paws may require treatment with a disinfectant spray to kill germs, as well as daily application of a topical antifungal lotion or spray. It may also be necessary to use an Elizabethan collar to keep the dog from licking the paws so they can stay dry while they heal.
Skin infections may require topical and oral treatment. Cleansing shampoos may clean up the greasy skin. Your vet may recommend using a medicated, antifungal shampoo and leaving it on the dogs skin for about 10 minutes. Bathing may need to be repeated for up to 12 weeks. The veterinarian will also prescribe an antifungal medication, as well as an antibiotic, to treat any bacterial skin infection that may occur along with yeast dermatitis.
How to Prevent Yeast Infections in Dogs
The good news is that yeast infections in dogs are not contagious to other dogs or humans. The most important thing to remember to prevent yeast infections is to keep the area clean and dry.
Too much moisture is a common cause of ear infections, so thoroughly drying your dogs ears after swimming and bathing can prevent moisture build-up. If your dog has a skin rash, musty smell, or is scratching or licking excessively, taking them to the veterinarian can prevent an infection from spreading and becoming more serious.
The prognosis for yeast infections is good when you follow the treatments your veterinarian gives you. Its important to understand that unless an underlying problem such as allergies, hypothyroidism, or seborrhea is controlled, a yeast infection is likely to come back.